Age-Related Variations in Anterior, Posterior, and Total Corneal Astigmatism
- PMID: 40808913
- PMCID: PMC12343332
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S531740
Age-Related Variations in Anterior, Posterior, and Total Corneal Astigmatism
Abstract
Introduction: Toric intraocular lens (IOL) calculation has traditionally relied on anterior corneal astigmatism (KA), but recent trends emphasize incorporating posterior corneal astigmatism (PCA) and total corneal astigmatism (TCA). However, age-related changes and sex-based differences in PCA and TCA remain inconclusive due to limited sample sizes in previous studies.
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional observational study using biometric measurements obtained with the IOLMaster 700. Patients with warning and failed history of corneal transplant or keratoconus were excluded. The objective was to evaluate age-related changes and sex-based differences in KA, PCA, and TCA among patients undergoing cataract surgery at a tertiary care center in Thailand.
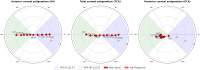
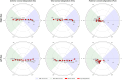
Results: A total of 23,932 eyes were analyzed for KA, and 9,546 eyes for PCA and TCA. Data were visualized using double-angle plots. PCA demonstrated a distinctive three-point star distribution, predominantly oriented along the with-the-rule (WTR) axis, with against-the-rule (ATR) astigmatism being rare in younger patients as illustrated in graphical abstract. Across KA, PCA, and TCA, the prevalence of ATR astigmatism increased in older age group, while WTR orientation decreased. A marked shift from WTR to ATR orientation was observed at different age thresholds: 60-65 years for KA, 75-80 years for PCA, and 55-65 years for TCA. KA and TCA also exhibited a preferential shift toward superonasal oblique orientation with advancing age-a pattern not observed in PCA. No significant sex-based differences were observed in mean astigmatism vector distributions across age groups.
Conclusion: Clinicians should account for age-related shifts in KA, PCA, and TCA when selecting toric IOLs, particularly in patients younger than 55 years. Preoperative counseling should address potential long-term shifts toward ATR orientation, which may influence visual outcomes in patients receiving toric IOLs aligned along other axes. Incorporating these changes into toric IOL formulae may improve patient outcomes.
Keywords: anterior corneal astigmatism; cataract surgery; corneal orientation; posterior corneal astigmatism; toric-IOL; total corneal astigmatism.
Plain language summary
In this study, we examined how the curvature and orientation of the cornea, specifically the anterior (front), posterior (back), and total corneal astigmatism, change with age and whether there are any differences between males and females. Astigmatism is when the cornea is not perfectly round, which can cause blurred vision. For patients undergoing cataract surgery, toric intraocular lenses (IOLs) are often used to correct this condition. Traditionally, surgeons have focused only on the front part of the cornea when planning for toric IOLs, but recent advances highlight the importance of also considering the back surface and total astigmatism of the cornea. By analyzing data from nearly 24,000 eyes, we discovered that astigmatism tends to shift in orientation as people age, from a with-the-rule (WTR) pattern commonly seen in younger patients to an against-the-rule (ATR) pattern in older adults. This shift happens at different ages for different layers of the cornea with changes showing as early as age 55. We also found that this shift often moves toward a nasal side in the front and total corneal surfaces, but not in the posterior surface. Importantly, we did not observe any meaningful differences between males and females. These findings suggest that age plays a significant role in determining astigmatism patterns and should be considered when selecting and aligning toric IOLs, especially for younger patients who may continue to experience changes in corneal shape over time. Discussing these potential future shifts with patients before surgery may help improve satisfaction and long-term visual outcomes.
© 2025 Pothikamjorn et al.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors declare any potential conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

