3D printing: Balancing innovation for sustainability with emerging environmental and health risks
- PMID: 40809003
- PMCID: PMC12343867
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.113185
3D printing: Balancing innovation for sustainability with emerging environmental and health risks
Abstract
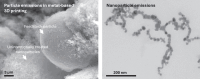
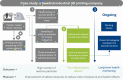
The rapid rise of 3D printing, both in industrial and home settings, presents emerging health and environmental risks. While 3D printing enhances sustainability by reducing waste and optimizing resource use, its impact on human health remains poorly understood. The use of metals and polymers linked to health risks, coupled with the release of inhalable particles and volatile organic compounds, raises concerns about respiratory and systemic effects. The absence of clear guidelines creates high public demand for information and limits safe implementation, particularly in schools and homes where millions of 3D printers are expected by 2030. Additionally, improper disposal of 3D printing polymer materials may exacerbate plastic pollution. This article proposes the perspective of a structured risk assessment framework set on particle emissions from industrial 3D printing. It will offer a practical tool to bridge current knowledge gaps and to inform safe practice and policy development, because immediate action is necessary to balance innovation with safety.
Keywords: Environmental health; Industrial engineering; Public health.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Ophthalmia Neonatorum.2025 Jul 7. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 7. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31855399 Free Books & Documents.
-
Accreditation through the eyes of nurse managers: an infinite staircase or a phenomenon that evaporates like water.J Health Organ Manag. 2025 Jun 30. doi: 10.1108/JHOM-01-2025-0029. Online ahead of print. J Health Organ Manag. 2025. PMID: 40574247
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Interventions to improve safe and effective medicines use by consumers: an overview of systematic reviews.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Apr 29;2014(4):CD007768. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007768.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24777444 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lengua C.A.G. In: Rapid prototyping in cardiac disease: 3D Printing the Heart. Farooqy K.M., editor. Springer; 2017. History of rapid prototyping; pp. 3–7.
-
- Mueller T., Elkaseer A., Charles A., Fauth J., Rabsch D., Scholz A., Marquardt C., Nau K., Scholz S.G. Eight weeks later—the unprecedented rise of 3D printing during the COVID-19 pandemic—a case study, lessons learned, and implications on the future of global decentralized manufacturing. Appl. Sci. 2020;10 doi: 10.3390/app10124135. - DOI
-
- Gebler M., Schoot Uiterkamp A.J.M., Visser C. A global sustainability perspective on 3D printing technologies. Energy Policy. 2014;74:158–167. doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2014.08.033. - DOI
-
- Srivastava M., Rathee S. Additive manufacturing: Recent trends, applications and future outlooks. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2022;7:261–287. doi: 10.1007/s40964-021-00229-8. - DOI
-
- Al Rashid A., Koç M. Additive manufacturing for sustainability and circular economy: needs, challenges, and opportunities for 3D printing of recycled polymeric waste. Mater. Today Sustain. 2023;24 doi: 10.1016/j.mtsust.2023.100529. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

