Predicting IDH and 1p/19q molecular status of gliomas with multi-b values DWI
- PMID: 40809035
- PMCID: PMC12344946
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1551023
Predicting IDH and 1p/19q molecular status of gliomas with multi-b values DWI
Abstract
Background and purpose: In the 2021 WHO Classification, the importance of molecular pathology in glioma diagnosis has been emphasized, particularly the status of isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) mutation and 1p/19q co-deletion. Advanced magnetic resonance diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) including mono-exponential (Mono), intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM), stretched exponential model (SEM) techniques are beneficial for non-invasive prediction of these molecular markers. The continuous-time random walk (CTRW) model mitigates the empirical nature of the SEM and has shown promising results in grading gliomas. However, the application of CTRW model in prediction of IDH and 1p/19q molecular phenotypes in adult diffuse gliomas remains underreported. This study compares the clinical utility of mono-exponential, IVIM, SEM, and CTRW models for predicting IDH and 1p/19q molecular status in adult diffuse gliomas.
Materials and methods: Data of adult diffuse glioma patients from January 2021 to August 2023 were collected. The multi-b-value DWI was acquired using a spin-echo echo-planar imaging sequence with 13 b-values (0, 10, 20, 30, 50, 70, 100, 150, 200, 400, 800, 1500, 2000 s/mm²) in 30 diffusion-encoding directions. Multi-b-value DWI images were post-processed to generate parametric maps based on the mono-exponential (Mono), the intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM), the stretched exponential model (SEM) and the continuous-time random walk (CTRW) models. The mean parameter values of solid tumor regions were calculated. An independent sample t-test or Mann-Whitney U test was used for comparisons between different subtypes of glioma. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analyses were used to assess diagnostic performance.
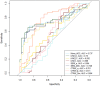
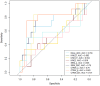
Results: A total of 95 glioma patients were included in the study. For predicting IDH status, CTRW_α exhibited the largest effect size and best diagnostic performance with an AUC of 0.761. At a threshold of 0.855, the sensitivity was 0.651, the specificity was 0.846, and the accuracy was 0.758. In predicting 1p/19q status in IDH-mutant gliomas, CTRW_α again showed the largest effect size and the best diagnostic performance with an AUC of 0.790. At a threshold of 0.886, sensitivity was 0.750, specificity was 0.903, and accuracy was 0.860.
Conclusions: The CTRW model could help predict IDH and 1p/19q status in adult diffuse gliomas.
Keywords: 1p/19q; IDH; continuous time random walk; diffusion magnetic resonance imaging; glioma.
Copyright © 2025 Zhao, Wang, Gao, Wang, Yang, Niu, Pan, Zhao, Cheng and Ma.
Conflict of interest statement
Author MW was employed by the company Siemens Healthineers Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Diagnostic test accuracy and cost-effectiveness of tests for codeletion of chromosomal arms 1p and 19q in people with glioma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Mar 2;3(3):CD013387. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013387.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35233774 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiation of Postoperative Tumor Recurrence and Pseudoprogression in Gliomas: A Comparative Study of Six Diffusion Models.Acad Radiol. 2025 Aug 6:S1076-6332(25)00705-6. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2025.07.036. Online ahead of print. Acad Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40774877
-
Diagnostic performance of deep learning for predicting glioma isocitrate dehydrogenase and 1p/19q co-deletion in MRI: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Radiol. 2025 Aug 16. doi: 10.1007/s00330-025-11898-2. Online ahead of print. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40817944
-
Continuous-time random walk and fractional order calculus models histogram analysis of glioma biomarkers, including IDH1, ATRX, MGMT, and TERT, on differentiation.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025 Jul 1;15(7):6118-6136. doi: 10.21037/qims-2024-2725. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025. PMID: 40727335 Free PMC article.
-
Radiogenomic association between the T2-FLAIR mismatch sign and IDH mutation status in adult patients with lower-grade gliomas: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Radiol. 2022 Aug;32(8):5339-5352. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-08607-8. Epub 2022 Feb 15. Eur Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35169897
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

