Association between neurodevelopmental disorders in congenital heart disease and changes in circulatory metabolites and gut microbiota composition
- PMID: 40809045
- PMCID: PMC12343688
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1639057
Association between neurodevelopmental disorders in congenital heart disease and changes in circulatory metabolites and gut microbiota composition
Abstract
Background: Neurodevelopmental disorder (ND) has emerged as a critical factor affecting the long-term quality of life among patients with congenital heart disease (CHD). The aim of this study was to provide a multi-omics perspective on the mechanisms of ND.
Methods: We analyzed the serum metabolome and gut microbiome of children with ND and non-ND (NND) in CHD populations.
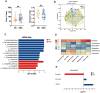
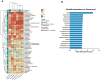
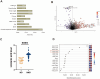
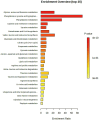
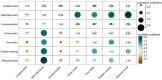
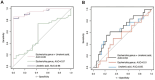
Results: In this prospective observational study, we identified associations between serum metabolites, gut microbial, and ND. Linolenic acid was most closely related to neurodevelopmental outcomes, showing positive correlations with multiple neurodevelopmental domains. Among the gut microbiota, the Escherichia genus was most strongly associated with neurodevelopmental outcomes, and negative correlations with neurodevelopmental domains.
Conclusion: This multi-omics study reveals significant association between altered serum metabolites, gut microbiota dysbiosis, and neurodevelopmental outcomes in children with CHD. The microbes and metabolites identified here may contribute to addressing the challenge of ND in the CHD population. Based on our findings, therapeutic strategies to reduce the risk of ND could be developed, including targeted manipulation of the gut microbiota and metabolites.
Keywords: congenital heart disease; gut microbiota; infant; metabolites; neurodevelopmental disorders.
Copyright © 2025 An, Wang, Bai, Ma, Yang, Yu and Mo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bucholz E. M., Sleeper L. A., Sananes R., Brosig C. L., Goldberg C. S., Pasquali S. K., et al. (2021). Trajectories in neurodevelopmental, health-related quality of life, and functional status outcomes by socioeconomic status and maternal education in children with single ventricle heart disease. J. Pediatr. 229, 289–293.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.09.066, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

