Intrathecal injections of non-peptide oxytocin receptor agonists, WAY 267,464 and TC OT 39, induce significant anti-hyperalgesia in both male and female rats with inflammatory pain
- PMID: 40809174
- PMCID: PMC12340419
- DOI: 10.22038/ijbms.2025.86093.18615
Intrathecal injections of non-peptide oxytocin receptor agonists, WAY 267,464 and TC OT 39, induce significant anti-hyperalgesia in both male and female rats with inflammatory pain
Abstract
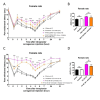
Objectives: Hyperalgesia is a clinical condition related to chronic pain in which patients experience increased nociceptive sensitivity. Intrathecal oxytocin has been shown to induce significant anti-hyperalgesia in both rodents and humans. However, in our previous studies, we demonstrated a clear sex difference in oxytocin's effects at the spinal level in rodents. We suggested that this sex difference could be partially due to the higher expression of the oxytocin-degrading enzyme, insulin-regulated aminopeptidase (IRAP), in the spinal cord of females. Thus, we aimed to evaluate non-peptide oxytocin receptor (OTR) agonists, which we speculated could effectively reduce inflammatory hyperalgesia in both sexes due to their resistance to IRAP degradation.
Materials and methods: Plantar tests were conducted on adult S.D. rats of both sexes to examine intraplantar carrageenan-induced hyperalgesia. This was followed by an intrathecal (i.t.) injection of non-peptide OTR agonists, WAY 267,464 and TC OT 39, to assess their effects on hyperalgesia. Atosiban, an OTR antagonist, was also co-administered with these compounds to confirm their involvement in OTR activation.
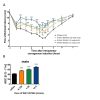
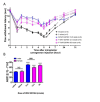
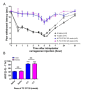
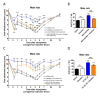
Results: WAY 267,464 and TC OT 39 were both effective in ameliorating anti-hyperalgesia in male and female rats, suggesting no sex difference. Additionally, atosiban attenuated the anti-hyperalgesia effects of WAY 267,464 and TC OT 39, confirming these compounds' involvement in OTR activation.
Conclusion: These compounds induced significant anti-hyperalgesia without any sex differences, suggesting that the inhibition of IRAP degradation eliminated the variation in oxytocin's effects based on sex. Therefore, we propose these compounds as promising candidates for treating inflammatory hyperalgesia in clinical applications.
Keywords: Hyperalgesia; Insulin-regulated- aminopeptidase; Oxytocin; Oxytocin receptor; Sex difference.
© 2025. This work is openly licensed via CC BY 4.0.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1(1):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. PMID: 31917873 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Oxytocin antagonists for assisted reproduction.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Sep 1;9(9):CD012375. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012375.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34467530 Free PMC article.
-
Discontinuation of intravenous oxytocin in the active phase of induced labour.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Aug 20;8(8):CD012274. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012274.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30125998 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xin Q, Bai B, Liu W. The analgesic effects of oxytocin in the peripheral and central nervous system. Neurochem Int. 2017;103:57–64. - PubMed
-
- Condes-Lara M, Martinez-Lorenzana G, Rojas-Piloni G, Rodriguez-Jimenez J. Branched oxytocinergic innervations from the paraventricular hypothalamic nuclei to superficial layers in the spinal cord. Brain Res. 2007;1160:20–29. - PubMed
-
- Yu SQ, Lundeberg T, Yu LC. Involvement of oxytocin in spinal antinociception in rats with inflammation. Brain Res. 2003;983:13–22. - PubMed
