Risk of remnant cholesterol and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a mendelian randomization study
- PMID: 40809208
- PMCID: PMC12340308
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-24-1894
Risk of remnant cholesterol and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a mendelian randomization study
Abstract
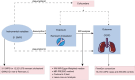
Background: Remnant cholesterol (RC) represents the cholesterol of triglyceride (TG)-rich lipoproteins and is the portion of cholesterol other than both high-density (HDL-C) and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C). Higher RC levels have been associated with heightened inflammation. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) has been attributed mostly to cigarette smoking or environmental pollution. Disorders of lipid metabolism contribute to inflammation, but no studies have shown an association between RC and COPD. We aimed to investigate the association between RC levels and the pathogenesis of COPD.
Methods: Pooled statistics for the associations between RC and COPD were obtained from published data of individuals of European ancestry, primarily sourced from the Integrative Epidemiology Unit (IEU) Open Genome-Wide Association Studies (OpenGWAS) project (including 115,078 European populations) and the FinnGen Biobank (including 16,410 COPD cases and 283,589 controls). To evaluate the causal relationship between RC and COPD, a two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis was employed. The primary MR method was inverse variance weighting (IVW). Statistical analysis and data visualization were performed using R software.
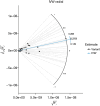
Results: RC levels were positively associated with COPD risk according to MR analysis [IVW, odds ratio (OR): 1.222, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.092-1.368; P<0.001; MR-Egger, OR: 1.279, 95% CI: 1.065-1.536; P=0.01; weighted median, OR: 1.208, 95% CI: 1.048-1.393; P=0.008]. No significant heterogeneity or horizontal pleiotropy was detected.
Conclusions: High RC levels might increase the risk of developing COPD. Whether reducing RC levels among the population contributes to a lower risk of COPD remains to be investigated.
Keywords: Mendelian randomization (MR); Remnant cholesterol (RC); chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD); triglycerides (TGs).
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jtd.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jtd-24-1894/coif). W.J.G. serves as an unpaid editorial board member of Journal of Thoracic Disease. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Causal Relationships Between Blood Lipid Levels and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Mendelian Randomization Analysis.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2025 Jan 8;20:83-93. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S476833. eCollection 2025. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2025. PMID: 39802042 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Causal Relationship Between Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Diabetes: A Bidirectional Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2025 Jul 4;20:2259-2272. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S516346. eCollection 2025. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2025. PMID: 40630676 Free PMC article.
-
A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study Investigating the Causal Relationship Between Ankylosing Spondylitis and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2025 Feb 8;20:259-271. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S491579. eCollection 2025. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2025. PMID: 39944597 Free PMC article.
-
Tiotropium versus long-acting beta-agonists for stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Sep 12;2012(9):CD009157. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009157.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22972134 Free PMC article.
-
Self-management interventions for people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jan 10;1(1):CD002990. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002990.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35001366 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Global Strategy for Prevention, Diagnosis and Management of COPD: 2024 Report. Available online: https://goldcopd.org/2024-gold-report/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
