State-of-the-art artificial intelligence methods for pre-operative planning of cardiothoracic surgery and interventions: a narrative review
- PMID: 40809213
- PMCID: PMC12340272
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-24-1793
State-of-the-art artificial intelligence methods for pre-operative planning of cardiothoracic surgery and interventions: a narrative review
Abstract
Background and objective: Artificial intelligence (AI) has been increasingly explored as a tool to enhance clinical decision-making and optimize and speed up preoperative planning in cardiothoracic surgery. By improving precision and efficiency, AI has the potential to streamline workflows and improve outcomes. This study aimed to examine the current applications of AI in preoperative planning for cardiothoracic procedures.
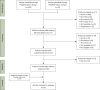
Methods: We systematically reviewed the literature in PubMed. Two search strings were employed to identify research articles related to AI applications in preoperative cardiothoracic surgery planning published up to August 2024. Studies were screened, and articles were included based on predefined criteria.
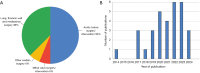
Key content and findings: A total of 525 articles were extracted from the PubMed database. After applying exclusion criteria and analyzing the articles, 32 articles were included. These articles were categorized into and described according to their application: aortic (valve) surgery/intervention, mitral valve surgery/intervention, other cardiac surgeries, and lung, thoracic wall, and mediastinal surgeries. Key AI applications included segmentation of anatomical structures, tumor detection, prosthesis sizing for transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI), and automated measurement of surgical parameters. The reviewed studies demonstrated that AI could increase segmentation accuracy, reduce preoperative planning time, and automate critical steps in surgical preparation.
Conclusions: AI has been introduced in preoperative planning for cardiothoracic procedures to support clinicians by increasing segmentation accuracy, reducing preoperative planning time, and automating several preoperative planning steps such as tumor detection, TAVI prosthesis sizing and other planning measurements. However, the widespread adoption faces several challenges, including the need for robust validation, regulatory approval, and integration into clinical workflows. Additionally, the implementation of AI involves substantial costs, including investments in software development, computational infrastructure, and training of clinical staff. Future research should focus not only on advancing AI technology but also on evaluating the cost-effectiveness to ensure it delivers measurable benefits while remaining accessible and sustainable for healthcare systems. Addressing these issues is essential to realize the full potential of AI in cardiothoracic surgery.
Keywords: Cardiothoracic surgery (CTS); artificial intelligence (AI); deep learning (DL); machine learning (ML); surgical planning.
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jtd.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jtd-24-1793/coif). Q.J.M. is a part-time employee of Surgical Reality. A.H.S. is a co-inventor of Surgical Reality. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
AI in Medical Questionnaires: Scoping Review.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Jun 23;27:e72398. doi: 10.2196/72398. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 40549427 Free PMC article.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
-
The measurement and monitoring of surgical adverse events.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(22):1-194. doi: 10.3310/hta5220. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532239
-
The impact of artificial intelligence on the endoscopic assessment of inflammatory bowel disease-related neoplasia.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2025 Jun 23;18:17562848251348574. doi: 10.1177/17562848251348574. eCollection 2025. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40556746 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
