A population-based nomogram for prognostic assessment in advanced lung cancer following progression with immune checkpoint inhibitor
- PMID: 40809275
- PMCID: PMC12340266
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-2025-165
A population-based nomogram for prognostic assessment in advanced lung cancer following progression with immune checkpoint inhibitor
Abstract
Background: The complexity of immunoresistance patterns in advanced lung cancer (LC) and the uniqueness of its efficacy response (e.g., pseudoprogression and hyperprogression) make it difficult to standardize treatment regimens after progression. This study aimed to analyze the independent factors after progression of immunotherapy in LC patients and to construct and validate a visual evaluation tool for assisting clinical prediction of prognosis.
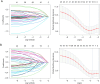
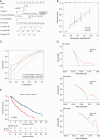
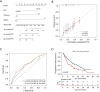
Methods: A total of 245 LC patients who progressed after receiving single or combination immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) therapy in Jinling Hospital, Affiliated Hospital of Medical School, Nanjing University between January 2019 and February 2024 were enrolled for retrospective analysis. The nomogram was created based on the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) and multivariate Cox regression analysis to predict overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) in R software. The time-dependent area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves (AUCs), calibration curves, and decision curve analysis (DCA) were used to assess the discrimination, accuracy, and clinical utility of the prediction models.
Results: Four independent factors significantly associated with OS were utilized to create a nomogram to predict OS: platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) level, smoking history, immune combination regimen, and liver metastasis factors. Three variables significantly associated with PFS were incorporated into the development of a nomogram for predicting PFS: PLR level, smoking history, and tumor stage. The results of the calibration curves showed that the predictive probabilities of the nomogram for OS and PFS were consistent with the observational data, with the C-indexes of the nomogram for predicting OS and PFS being 0.643 [95% confidence interval (CI): 0.592-0.695] and 0.588 (95% CI: 0.541-0.636), respectively. The AUCs for predicting the 12-month, 24-month, and 36-month OS and PFS were 0.681 and 0.763, 0.795 and 0.637, 0.649 and 0.694, respectively. The DCA curves indicated that the nomogram for OS had good net benefits. Compared to the high-risk group, the OS and PFS were significantly prolonged in the low-risk group.
Conclusions: The novel nomogram for predicting the prognosis of advanced LC patients after progression with ICIs provides a scientific basis and an important reference for the development of individualized treatment strategies. Our study revealed that PLR level, smoking history, and liver metastasis were significant prognostic indicators. In the future, specific treatment options that could prolong patients' OS and PFS need to be further explored.
Keywords: Lung cancer (LC); immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs); nomogram; prognosis.
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jtd.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jtd-2025-165/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A SEER prognostic nomogram analysis for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: comparing the immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) and non-ICIs eras.J Thorac Dis. 2025 May 30;17(5):2866-2887. doi: 10.21037/jtd-2024-1981. Epub 2025 May 28. J Thorac Dis. 2025. PMID: 40529760 Free PMC article.
-
Are Current Survival Prediction Tools Useful When Treating Subsequent Skeletal-related Events From Bone Metastases?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Sep 1;482(9):1710-1721. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003030. Epub 2024 Mar 22. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 38517402
-
A novel nomogram for predicting osteoporosis with low back pain among the patients in Wenshan Zhuang and Miao Autonomous Prefecture of China.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 5;16:1535163. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1535163. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40538801 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
Nivolumab for adults with Hodgkin's lymphoma (a rapid review using the software RobotReviewer).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 12;7(7):CD012556. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012556.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30001476 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Cancer Society Lung Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging. Accessed on 24 April 2025. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/lung-cancer/detection-diagnosis-stag...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
