The impact of donor-recipient size mismatch on lung transplant outcomes
- PMID: 40809276
- PMCID: PMC12340290
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-24-1841
The impact of donor-recipient size mismatch on lung transplant outcomes
Abstract
Background: Lung transplantation (LT) represents a critical therapeutic intervention for advanced chronic lung diseases. This study aims to elucidate the prognostic implications of donor-recipient size matching, specifically focusing on the ratio of predicted total lung capacity (pTLC).
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort analysis of 380 transplant recipients at a single LT center from January 2015 to October 2023. Patients were stratified based on size discrepancies exceeding 10% and 20%, calculated using two established formulas.
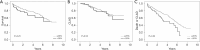
Results: Our findings indicate that significant size mismatches do not correlate with adverse post-transplant outcomes, including primary graft dysfunction (PGD), duration of mechanical ventilation, or overall survival rates. Notably, a size discrepancy greater than 20% utilizing the first formula emerged as an independent risk factor for the composite outcome of chronic lung allograft dysfunction (CLAD) and mortality. While the majority of donor-recipient pairings were of the same sex, sex mismatch significantly influenced size discrepancies. Furthermore, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients demonstrated elevated pTLC ratios compared to those with interstitial lung disease (ILD), underscoring the complexity inherent in size matching across different pathologies.
Conclusions: Our data suggests that significant size discrepancies between donor and recipient do not adversely impact immediate outcomes in LT recipients, but it may have significant long-term implications; therefore, appropriate donor size selection for each recipient is essential. The use of pTLC formulas can be helpful for estimating the suitable size.
Keywords: Size matching; chronic lung allograft dysfunction (CLAD); donor; lung transplantation (LT); recipient.
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jtd.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jtd-24-1841/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sex and gender as predictors for allograft and patient-relevant outcomes after kidney transplantation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Dec 19;12(12):CD014966. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014966.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39698949
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Cyclophosphamide for connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 3;1(1):CD010908. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010908.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29297205 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions to reduce harm from continued tobacco use.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Oct 13;10(10):CD005231. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005231.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27734465 Free PMC article.
-
Does Augmenting Irradiated Autografts With Free Vascularized Fibula Graft in Patients With Bone Loss From a Malignant Tumor Achieve Union, Function, and Complication Rate Comparably to Patients Without Bone Loss and Augmentation When Reconstructing Intercalary Resections in the Lower Extremity?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 Jun 26. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003599. Online ahead of print. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 40569278
References
-
- Hussain M, Thornton M, Hussain T, et al. Evaluating the Use of CT-Derived Lung Volumes in Donor-Recipient Lung Size Matching for Lung Transplantation in Patients With Interstitial Lung Disease and/or Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Transplant Proc 2023;55:623-8. 10.1016/j.transproceed.2023.02.059 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chambers DC, Cherikh WS, Harhay MO, et al. The International Thoracic Organ Transplant Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: Thirty-sixth adult lung and heart-lung transplantation Report-2019; Focus theme: Donor and recipient size match. J Heart Lung Transplant 2019;38:1042-55. 10.1016/j.healun.2019.08.001 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous