Neutrophils loaded NAD+ impede TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway for sepsis treatment
- PMID: 40809343
- PMCID: PMC12345315
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.102168
Neutrophils loaded NAD+ impede TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway for sepsis treatment
Abstract
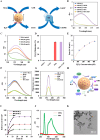
Systemic inflammation, excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) and mitochondrial impairment are the main cause of multi-organ dysfunction syndrome in sepsis. Nevertheless, the pharmaceuticals currently in development focus solely on a single mechanism of disease, which is evidently inadequate. Herein, a precision nanodrug delivery system (MSe-NAD+/Nes) has been designed, incorporating mesoporous selenium nanozymes (MSe NPs) and leveraging a neutrophil-targeting strategy, to accomplish accurate delivery and mitigate inflammation. Upon reaching the inflammatory region, MSe NPs destroys selenium bonds and releases NAD+ under the action of ROS, which in turn supplements the NAD+ pool and promotes the recovery of mitochondrial function. Moreover, MSe NPs are capable of efficiently eliminating ROS by mimicking the activity of glutathione peroxidase (GPx), thus preventing the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. In vivo administration has indicated that MSe-NAD+/Nes efficiently alleviates organ oxidative stress, restores ATP levels, attenuates systemic hyperinflammation, and facilitates rapid organ repair. This study presents a potential modality of inflammation remission via ROS scavenging and mitochondrial repairment for the reliable and safe therapy of sepsis.
Keywords: Inflammation; NAD+; Neutrophil; ROS; Sepsis.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures






References
-
- Huang B., Zhang N., Qiu X., Zeng R., Wang S., Hua M., Li Q., Nan K., Lin S. Mitochondria-targeted SkQ1 nanoparticles for dry eye disease : inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation by preventing mitochondrial DNA oxidation. J. Contr. Release. 2024;365:1–15. - PubMed
-
- Nandi D., Debnath M., Iii J.F., Pandey A., Bharadwaj H., Patel R., Kulkarni A. Nanoparticle-mediated co-delivery of inflammasome inhibitors provides protection against sepsis. Nanoscale. 2024;16:4678–4690. - PubMed
-
- Liu F., Zhang K., Lu B., Wang X., Dong Q., Xue T., Tan Y., Wang X., Du J. Oxygen-vacancy-rich monolayer BiO 2- x nanosheets for bacterial sepsis management via dual physically antibacterial and chemically anti-inflammatory functions. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2024;13 - PubMed
-
- Wendel M., Heller A.R. Mitochondrial function and dysfunction in sepsis, Wien. Med. Wochenschr. 2010;160:118–123. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

