METTL1 in human cancers: recognition of their functions, mechanisms and therapeutic value
- PMID: 40809384
- PMCID: PMC12343562
- DOI: 10.3389/or.2025.1637372
METTL1 in human cancers: recognition of their functions, mechanisms and therapeutic value
Abstract
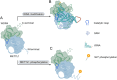
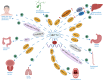
Methyltransferase-like 1 (METTL1) is a methyltransferase that modulates the RNA methylation process and has been increasingly investigated in cancer research over the past decade. The review aims to summarize the diverse roles of METTL1 in various cancers, focusing on the mechanisms underlying tumorigenesis, progression, and metastasis. Furthermore, the therapeutic value and targeting strategies for METTL1 are also discussed to provide the foundation for further development of METTL1-targeted therapies. The article integrates recent research findings to highlight significant discoveries regarding METTL1, emphasizing its potential as a therapeutic target in cancer treatment.
Keywords: METTL1; RNA methylation; cancer; therapeutic target; tumor mechanism.
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Chen, Li, Zhou and Song.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
METTL1-mediated m7G modification of NEK1 mRNA promotes the proliferation of oral squamous cell carcinoma.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2025 Oct;1871(7):167961. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2025.167961. Epub 2025 Jun 23. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2025. PMID: 40562282
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Exploring the role of m7G modification in Cancer: Mechanisms, regulatory proteins, and biomarker potential.Cell Signal. 2024 Sep;121:111288. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111288. Epub 2024 Jul 5. Cell Signal. 2024. PMID: 38971569 Review.
-
METTL1-WDR4 promotes the migration and proliferation of gastric cancer through N7-methylguanosine.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2025 Aug 5. doi: 10.1007/s13402-025-01094-1. Online ahead of print. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2025. PMID: 40764449
-
A narrative review of epigenetic marker in H3K27ac and its emerging potential as a therapeutic target in cancer.Epigenomics. 2025 Mar;17(4):263-279. doi: 10.1080/17501911.2025.2460900. Epub 2025 Feb 21. Epigenomics. 2025. PMID: 39981972 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

