A Comprehensive Review on Recent Advances in Plant Flour-Based Edible Tableware
- PMID: 40809385
- PMCID: PMC12350001
- DOI: 10.1155/ijbm/6206991
A Comprehensive Review on Recent Advances in Plant Flour-Based Edible Tableware
Abstract
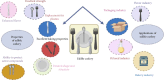
Nowadays, plastic has become an integral part of our daily used products. Packaging is the sector where a significant portion of plastics are being used, and it has increased many folds after the recent pandemic. The plastic-based cutlery, cups, bowls, and plates have been commonly used in ready-to-eat packaged food, and they include mostly single-use plastic; thus, there is an urgent need for substitution with eco-friendly alternatives. The edible cups, bowls, and cutlery could be a promising alternative to the plastic counterparts. This review debated the current scenario in edible cutlery fabrication and characterization. The plant-based, eco-friendly edible flour materials are commonly used for fabricating edible cutlery such as bowls, cups, and spoons. The fortification and enrichment of additives into the edible cutlery and tableware were promising to improve the physical and functional performance. To develop edible cutlery, various flours such as millet, wheat, and rice have already been explored, and the results are promising for attaining sustainable development. The edible spoons prepared by using various flours such as finger millet and wheat flour with ashwagandha powder showed high proximate composition, including protein 5.96% and carbohydrates 85.73%. Similarly, the edible cutlery prepared using rice flour, wheat flour, and banana blossom powder resulted in a high water absorption capacity of 31.59% and showed high biodegradable capacity and decayed in 5 days. The use of this edible tableware not only reduces plastic waste issues but also makes our food healthier and nutrition-rich. Hence, this review aims to provide an overview of edible cutlery's needs and current status.
Keywords: biodegradable; edible cutlery; food; packaging; plastic waste; sustainable.
Copyright © 2025 Swarup Roy et al. International Journal of Biomaterials published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Portion, package or tableware size for changing selection and consumption of food, alcohol and tobacco.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Sep 14;2015(9):CD011045. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011045.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26368271 Free PMC article.
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Interventions to improve safe and effective medicines use by consumers: an overview of systematic reviews.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Apr 29;2014(4):CD007768. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007768.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24777444 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cera A., Cesarini G., Scalici M. Microplastics in Freshwater: What is the News From the World? Diversity . 2020;12(7):p. 276. doi: 10.3390/d12070276. - DOI
-
- Navarre N., Mogollón J. M., Tukker A., Barbarossa V. Recycled Plastic Packaging From the Dutch Food Sector Pollutes Asian Oceans. Resources, Conservation and Recycling . 2022;185:p. 106508. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2022.106508. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

