Molecular identification and genotyping of Blastocystis in farmed Cattle, Goats, and Pigs from Zhejiang Province, China
- PMID: 40809407
- PMCID: PMC12347955
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fawpar.2025.e00280
Molecular identification and genotyping of Blastocystis in farmed Cattle, Goats, and Pigs from Zhejiang Province, China
Abstract
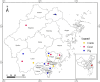
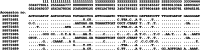
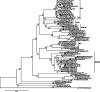
Blastocystis is a genus of parasitic protozoa that parasitize/colonize humans and animals gastrointestinal tract. The current study performed a molecular survey of Blastocystis in farm cattle (Bos tarurs), goats (Capra hircus), and pigs (Susscrofa domestica) raised in different cities in Zhejiang Province of China to better understand the epidemiology of Blastocystis in the animals of this region. A total of 859 fresh fecal samples were collected from 265 cattle, 386 goats, and 208 pigs. All these samples were screened for the detection of Blastocystis by amplifying the small subunit ribosomal RNA (SSU rRNA) gene via PCR and Sanger sequencing. Of the 859 samples tested, 12.1 % (104) were positive for Blastocystis, with cattle showing a prevalence of 19.6 % (52/265), goats with 11.4 % (44/386), and pigs with 3.8 % (8/208). Eight different subtypes of Blastocystis were found: ST10 (n = 51), ST5 (n = 11), ST12 (n = 9), ST14 (n = 8), ST21 (n = 8), ST23 (n = 7), ST26 (n = 6), and ST4 (n = 4). Cattle carried seven (ST5, ST10, ST12, ST14, ST21, ST23, and ST26), whereas goats harbored eight (ST4, ST5, ST10, ST12, ST14, ST21, ST23, and ST26) subtypes. All pig-derived Blastocystis isolates belonged only to ST5. These results are significant as they indicate that cattle, goats, and pigs in Zhejiang Province, China, harbor various subtypes of Blastocystis, which enhances our understanding of the distribution of Blastocystis among these hosts in China.
Keywords: Blastocystis; Cattle; China; Genotypic variation; Goat; Pig.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. on behalf of International Association of Food and Waterborne Parasitology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Asghari A., Sadrebazzaz A., Shamsi L., Shams M. Global prevalence, subtypes distribution, zoonotic potential, and associated risk factors of Blastocystis sp. in domestic pigs (Sus domesticus) and wild boars (Sus scrofa): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Microb. Pathog. 2021;160 - PubMed
-
- Asghari A., Yousefi A., Mohammadi M.R., Badali R., Shamsi L., Köseoğlu A.E., Abbaszadeh A., Shams M., Mohammadi-Ghalehbin B. Comparative molecular epidemiology, subtype distribution, and zoonotic potential of Blastocystis sp. in Equus animals (horses, donkeys, and mules) in northwestern Iran. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2024;106 - PubMed
-
- Barati M., KarimiPourSaryazdi A., Rahmanian V., Bahadory S., Abdoli A., Rezanezhad H., Solhjoo K., Taghipour A. Global prevalence and subtype distribution of Blastocystis sp. in rodents, birds, and water supplies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Prev. Vet. Med. 2022;208 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

