Mechanical Agitation-Assisted Transmembrane Drug Delivery by Magnetically Powered Spiky Nanorobots
- PMID: 40809455
- PMCID: PMC12349924
- DOI: 10.34133/research.0768
Mechanical Agitation-Assisted Transmembrane Drug Delivery by Magnetically Powered Spiky Nanorobots
Abstract
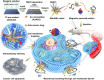
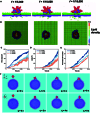
Breaking through cell membrane barriers is a crucial step for intracellular drug delivery in antitumor chemotherapy. Hereby, a magnetic nanorobot, capable of exerting mechanical agitation on cellular membrane to promote intracellular drug delivery, was developed. The main body of the nanorobots was composed of nano-scaled gold nanospikes that were deposited with Ni and Ti nanolayers for magnetic activation and biocompatibility, responsively. The nanorobots can be precisely navigated to target cancer cells under external magnetic field control. By virtue of the sharp nanospike structures, the magnetically powered rotation behavior of the nanorobots can impose mechanical agitation on the living cell membrane and thus improve the membrane permeability, leading to promoted transmembrane cargo delivery. Coarse-grained molecular dynamics simulation revealed that the mechanism of mechanical intervention regulated permeability of the bilayer lipid membrane, allowing for enhanced transmembrane diffusion of small cargo molecules. An in vitro study demonstrated that these nanorobots can markedly enhance the efficiency of drug entry into tumor cells, thus improving the effectiveness of tumor therapy under magnetic activation in vivo. This work paves a new way for overcoming cell membrane barriers for intracellular drug delivery by using a magnetic nanorobotic system, which is expected to promote further application of magnetically controlled nanorobot technology in the field of precision medicine.
Copyright © 2025 Xiaojia Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Wang L, Zhu X, Xu C, Jin D, Ma X. Artificial breakthrough of cell membrane barrier for transmembrane substance exchange: A review of recent progress. Adv Funct Mater. 2024;34(13):2311920.
-
- Xie J, Shen Q, Huang K, Zheng T, Cheng L, Zhang Z, Yu Y, Liao G, Wang X, Li C. Oriented assembly of cell-mimicking nanoparticles via a molecular affinity strategy for targeted drug delivery. ACS Nano. 2019;13(5):5268–5277. - PubMed
-
- Oroojalian F, Beygi M, Baradaran B, Mokhtarzadeh A, Shahbazi MA. Immune cell membrane-coated biomimetic nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. Small. 2021;17(12):2006484. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

