IL-4 and IL-13 in Cardiovascular Disease: From Immune Modulation to Therapeutic Possibilities - A Narrative Review
- PMID: 40809465
- PMCID: PMC12343335
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S531346
IL-4 and IL-13 in Cardiovascular Disease: From Immune Modulation to Therapeutic Possibilities - A Narrative Review
Abstract
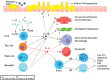
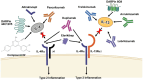
Background: Interleukin-4 (IL-4) and Interleukin-13 (IL-13) are central regulators of the Th2 immune response and play pivotal roles in vascular inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, and cardiovascular remodeling. While their contributions to immune modulation are well known, their precise effects on the cardiovascular system remain an evolving field of study.
Aim: This review aims to explore the mechanistic roles of IL-4 and IL-13 in endothelial dysfunction and the development of cardiovascular diseases, and to evaluate the therapeutic potential and risks associated with IL-4/IL-13 inhibitors.
Methods: A narrative review approach was used. Articles published between 2015 and 2025 were identified through PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar using relevant keywords. Mechanistic, experimental, and clinical studies examining IL-4/IL-13 signaling and inhibitor outcomes were selected.
Results: IL-4 and IL-13 contribute to vascular inflammation by upregulating adhesion molecules, disrupting nitric oxide synthesis via arginase I, and increasing oxidative stress. These cytokines promote vascular remodeling and are linked to hypertension, atherosclerosis, and cardiac fibrosis. Inhibitors like dupilumab show promise in controlling inflammation, but their long-term cardiovascular effects remain unclear. Some studies suggest potential risks such as increased infections, metabolic dysregulation, and vascular stiffening.
Conclusion: IL-4 and IL-13 are active mediators in cardiovascular pathology, offering both therapeutic potential and clinical challenges. While inhibitors targeting these cytokines may reduce inflammation, their broader impacts on vascular health warrant cautious and personalized application until long-term cardiovascular outcomes are clarified through further research.
Keywords: IL-13; IL-4; cardiovascular disease; cytokine inhibition; endothelial dysfunction.
© 2025 Kılıç et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interventions to improve safe and effective medicines use by consumers: an overview of systematic reviews.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Apr 29;2014(4):CD007768. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007768.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24777444 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources