Clonal abundance patterns in hematopoiesis: Mathematical modeling and parameter estimation
- PMID: 40809480
- PMCID: PMC12342013
- DOI: 10.3389/fsysb.2023.893366
Clonal abundance patterns in hematopoiesis: Mathematical modeling and parameter estimation
Abstract
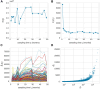
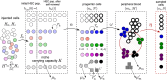
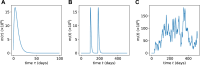
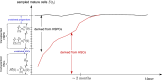
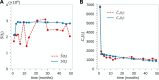
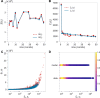
Hematopoiesis has been studied via stem cell labeling using barcodes, viral integration sites (VISs), or in situ methods. Subsequent proliferation and differentiation preserve the tag identity, thus defining a clone of mature cells across multiple cell type or lineages. By tracking the population of clones, measured within samples taken at discrete time points, we infer physiological parameters associated with a hybrid stochastic-deterministic mathematical model of hematopoiesis. We analyze clone population data from Koelle et al. (Koelle et al., 2017) and compare the states of clones (mean and variance of their abundances) and the state-space density of clones with the corresponding quantities predicted from our model. Comparing our model to the tagged granulocyte populations, we find parameters (stem cell carrying capacity, stem cell differentiation rates, and the proliferative potential of progenitor cells, and sample sizes) that provide reasonable fits in three out of four animals. Even though some observed features cannot be quantitatively reproduced by our model, our analyses provides insight into how model parameters influence the underlying mechanisms in hematopoiesis. We discuss additional mechanisms not incorporated in our model.
Keywords: barcodes; clonal tracking; differentiation; hematopoiesis; stem cells.
Copyright © 2023 Pan, D’Orsogna, Tang, Stiehl and Chou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Longitudinal clonal tracking in humanized mice reveals sustained polyclonal repopulation of gene-modified human-HSPC despite vector integration bias.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Oct 7;12(1):528. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02601-5. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34620229 Free PMC article.
-
Factors that influence parents' and informal caregivers' views and practices regarding routine childhood vaccination: a qualitative evidence synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Oct 27;10(10):CD013265. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013265.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34706066 Free PMC article.
-
Falls prevention interventions for community-dwelling older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits, harms, and patient values and preferences.Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02681-3. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39593159 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity and seroefficacy of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Jul;28(34):1-109. doi: 10.3310/YWHA3079. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39046101 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Attar A. (2014). Changes in the cell surface markers during normal hematopoiesis: A guide to cell isolation. Glob. J. Hematol. Blood Transfus. 1, 20–28. 10.15379/2408-9877.2014.01.01.4 - DOI
-
- Bortz A. B., Kalos M. H., Lebowitz J. L. (1975). A new algorithm for Monte Carlo simulation of ising spin systems. J. Comput. Phys. 17, 10–18. 10.1016/0021-9991(75)90060-1 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
