The diagnostic potential of extracellular vesicles in virus-related diseases
- PMID: 40809518
- PMCID: PMC12343271
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1641405
The diagnostic potential of extracellular vesicles in virus-related diseases
Abstract
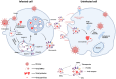
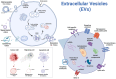
Extracellular vesicles (EVs), a heterogeneous population of lipid bilayer-enclosed membranous particles, are widely involved in cell-cell communication and pathophysiological regulation. Recent advances reveal their dual functionality in viral pathogenesis: while facilitating viral dissemination through transport of pathogenic components, they simultaneously orchestrate host antiviral defense mechanisms. The unique molecular cargo loading capacity and high stability of EVs in body fluids make them ideal biomarkers for early infection diagnosis, treatment monitoring, and prognostic evaluation of virus-related disease. Compared to traditional viral detection methods, EV-based liquid biopsy techniques exhibit distinct advantages, including non-invasiveness and enhanced sensitivity thresholds. This review systematically examines the diagnostic potential of EV biomarkers in viral infections, offering novel perspectives for developing precision diagnostics and therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: biomarker; diagnosis; extracellular vesicles; virus; virus-related diseases.
Copyright © 2025 Gao, Zhan, Zhang, Sun, Xiang, Bao, Gao, Zhang, Wang and Mao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Block L. N., Schmidt J. K., Keuler N. S., McKeon M. C., Bowman B. D., Wiepz G. J., et al. (2022). Zika virus impacts extracellular vesicle composition and cellular gene expression in macaque early gestation trophoblasts. Sci. Rep. 12, 7348. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-11275-9, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical