Prevalence of unmet need for family planning and unintended pregnancies among women of reproductive age living with HIV in sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40809560
- PMCID: PMC12341186
- DOI: 10.4314/ahs.v24i2.6
Prevalence of unmet need for family planning and unintended pregnancies among women of reproductive age living with HIV in sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Family planning is an effective intervention for women living with HIV who do not desire to have children to reduce vertical transmission and infant- and pregnancy-related mortality.
Objectives: We aimed to evaluate the prevalence of unmet need for family planning (UFP) and unintended pregnancies among women living with HIV in sub-Saharan Africa.
Methods: This was a systematic review that searched databases from March 2007 to December 2021. UFP was defined as women who were sexually active and did not desire to have additional children (unmet need for limiting), or who delayed their next pregnancy (unmet need for spacing) but were not using any contraception. Unintended pregnancies were defined as women who reported that their last pregnancy was unintended. Forest plots were used to present the pooled prevalence with a 95% confidence interval (CI).
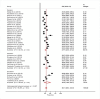
Results: Total of 35 articles were included. Overall, the pooled prevalence of UFP was 30.1% (95%CI, 26.4-33.9). The pooled prevalence of unmet need for spacing was 11.9% and 14.2% for limiting.. The pooled prevalence of unintended pregnancy was 16.5% (95%CI, 9.4-25.1).
Conclusion: Three in ten women of reproductive age living with HIV in Africa have UFP. Efforts to prevent unsafe abortions from unintended pregnancies are needed to minimize the UFP.
Keywords: Unmet need for family planning; sub-Saharan Africa; un intended pregnancy; women living with HIV.
© 2024 Bakari HM et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- WHO, author. Summary of global HIV epidemic. 2021. [Available from: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/hiv-aids .
-
- WHO, author. Mother-to-child transmission of HIV. 2019. [Available from: https://www.who.int/teams/global-hiv-hepatitis-and-stis-programmes/hiv/p... .
-
- Reynolds HW, Janowitz B, Homan R, Johnson L. The value of contraception to prevent perinatal HIV transmission. Sex Transm Dis. 2006;33(6):350–356. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
