Machine learning-assisted rational design and evolution of novel signal peptides in Yarrowia lipolytica
- PMID: 40809675
- PMCID: PMC12348225
- DOI: 10.1016/j.synbio.2025.07.008
Machine learning-assisted rational design and evolution of novel signal peptides in Yarrowia lipolytica
Abstract
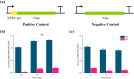
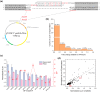
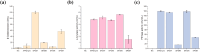
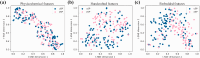
Microbial proteins hold great promise as sustainable alternatives for future protein sources, and oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica has emerged as a recognized platform for heterologous protein expression and secretion. N-terminal signal peptides (SPs) are crucial for directing proteins to the secretion pathway, which offers advantages in both academic and industrial protein production. Although some of the innate SPs of Y. lipolytica have been reported, there is a growing need to expand the genetic toolkit of SPs to support the increasing use of Y. lipolytica as a cell factory for overproduction of various secretory proteins. In this study, we employed an efficient evolutionary approach to rapidly evolve the innate SP XPR2-pre by leveraging Gibson assembly with two synthetic overlapping oligos containing high portion of degenerate nucleotides. Using Nanoluc (Nluc) luciferase as a robust reporter, we characterized the intracellular and extracellular enzymatic activity of 447 SP mutants and identified previously undescribed SPs exhibiting superior performance compared to XPR2-pre in Nluc luciferase secretion, with improvements of up to 2.91-fold of enzymatic activity in the supernatant. The generalizability of the top-performing SPs was evaluated using three additional heterologous enzymes (β-galactosidase, α-amylase, and PET hydrolase). Our results confirmed their versatility across different proteins with protein-specific efficiency. Additionally, based on our screening, we also evaluated the performance of different feature engineering strategies and machine learning models in the design and prediction of SP mutants. This study integrated rational design, directed evolution and machine learning to identify novel SPs, expanding the repertoire of signal peptides and benefiting secretory protein overexpression in Y. lipolytica.
Keywords: Directed evolution; Machine learning; Protein secretion; Rational Design; Siganl peptides; Yarrowia lipolytica.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this manuscript. The research was conducted independently, and no financial or personal relationships influenced the results and discussions presented in the paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enhancing selective itaconic acid synthesis in Yarrowia lipolytica through targeted metabolite transport reprogramming.Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2025 Jun 19;18(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s13068-025-02668-9. Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2025. PMID: 40537803 Free PMC article.
-
New Yarrowia lipolytica chassis strains for industrial enzyme production.Microb Cell Fact. 2025 Jul 10;24(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s12934-025-02787-w. Microb Cell Fact. 2025. PMID: 40640804 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- GVR, Recombinant Proteins Market Size . 2021. Share & Trends Analysis Report by Host Cell (Insect Cells, Mammalian), by Application (Research, Therapeutics), by Product & Services, by End-User, by Region, and Segment Forecasts; pp. 2022–2030.
-
- Thak E.J., et al. Yeast synthetic biology for designed cell factories producing secretory recombinant proteins. FEMS Yeast Res. 2020;20(2):foaa009. - PubMed
-
- Ma J., et al. Synthetic biology, systems biology, and metabolic engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica toward a sustainable biorefinery platform. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020;47(9-10):845-862 - PubMed
-
- López-Trujillo J., et al. Temperature and pH optimization for protease production fermented by Yarrowia lipolytica from agro-industrial waste. Fermentation. 2023;9(9):819.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

