The status of p53 affects the efficacy of PLK1 inhibitor BI6727 in prostate cancer cells
- PMID: 40809688
- PMCID: PMC12343621
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1602693
The status of p53 affects the efficacy of PLK1 inhibitor BI6727 in prostate cancer cells
Abstract
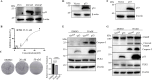
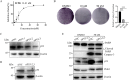
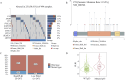
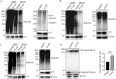
As there are no effective treatments for advanced prostate cancer, exploring new therapies is crucial. BI6727(Volasertib), a PLK1 inhibitor, shows great promise as an anti-cancer drug. However, despite advancing to phase II and III trials in other cancers, BI6727 has shown limited anti-tumor activity in prostate cancer, making it crucial to investigate the underlying reasons for this discrepancy. In this study, we found that the status of p53 affects the sensitivity of prostate cancer cells to BI6727. Prostate cancer cells PC3 (long-term loss of p53 expression), DU145 (expressing mutant-type p53) and LNCaP (expressing wild-type p53) were treated with BI6727, respectively. It was found that PC3 cells were more sensitive to BI6727 when wild-type p53 was introduced into these cancer cells; while apoptosis induced by BI6727 was reduced after knockdown of p53 in LNCaP cells. In additional, in DU145 cells, the presence of points mutation in p53 exerted a dominant negative effect, attenuating BI6727-induced apoptosis. Further analysis revealed that missense mutations in the P53 gene are widespread in prostate cancer patients. Mechanistically, BI6727 reduces the degradation of Topors, thereby increasing the stability of p53 by reducing its ubiquitination. This ultimately influences the sensitivity of prostate cancer cells with different p53 statuses to BI6727.In summary, this study identifies p53 as a key factor limiting the clinical efficacy of BI6727 in prostate cancer cells.
Keywords: BI6727; PLK1; PLK1 inhibitor; p53; prostate cancer.
Copyright © 2025 Li, Wang, Guo and Wen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1(1):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. PMID: 31917873 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

