Regulatory role of E3 ubiquitin ligases in multiple myeloma: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic strategies
- PMID: 40809696
- PMCID: PMC12343653
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1620097
Regulatory role of E3 ubiquitin ligases in multiple myeloma: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic strategies
Abstract
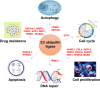
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a hematological tumor characterized by the malignant proliferation of plasma cells in bone marrow (BM). Despite the prolonged survival of MM patients, a significant amount of patients relapse or become drug resistant. This underlines the importance of the development and investigation of novel targets to improve MM therapy. Increasing evidences have shed light on the emerging roles of E3 ubiquitin ligases in MM. E3 ubiquitin ligases play an essential role in protein ubiquitination, which is involved in the regulation of protein degradation, protein-protein interactions and signal transduction. In this comprehensive review, we will summarize the current understanding of E3 ubiquitin ligases in MM and their contribution to MM therapy, which could help explore the molecular mechanisms in MM and provide potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of MM.
Keywords: E3 ubiquitin ligases; immunity; multiple myeloma; pathogenesis; therapeutic targets.
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Zhou, Dong, Xu and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Amatangelo M., Flynt E., Stong N., Ray P., Van Oekelen O., Wang M., et al. (2024). Pharmacodynamic changes in tumor and immune cells drive iberdomide's clinical mechanisms of activity in relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma. Cell Rep. Med. 5 (6), 101571. 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101571 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources