A Common Genetic Background for Psoriasis and Cardiovascular Diseases: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 40809699
- PMCID: PMC12344513
- DOI: 10.1002/hsr2.71128
A Common Genetic Background for Psoriasis and Cardiovascular Diseases: A Narrative Review
Abstract
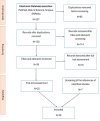
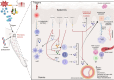
Background and aims: Psoriasis is an immune-mediated disease affecting primarily the skin and joints, but which also has systemic implications. There are assumptions about a common genetic background between psoriasis and cardiovascular diseases. This narrative review aims to provide an overview of the existing data regarding the IL-23 rs2066808, IL-23R rs2201841, IL-17RA rs4819554, and IL-17A rs2275913 polymorphisms and their link to psoriasis and cardiovascular diseases.
Methods: PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, and "SNPedia" searches were conducted to identify the relevant studies between 2007 and 2025 that investigated the association between psoriasis, cardiovascular diseases, and the IL-23 rs2066808, IL-23R rs2201841, IL-17RA rs4819554, and IL17A rs2275913 polymorphisms.
Results: The existing data are conflicting. The polymorphisms could be implicated in psoriasis onset, disease susceptibility, and treatment response. Some of them are also linked to coronary artery disease. Contradictory data could result from the heterogeneity of the population included in the studies and the laboratory techniques used for polymorphism determination.
Conclusion: The interplay between IL-17, IL-23, and genetic polymorphisms illustrates a complex landscape in psoriasis and its associated comorbidities. More standardized case-control studies are needed to confirm this hypothesis. Moreover, extensive studies in diverse populations would be important to clarify these relationships and the potential implications for treatment and management.
Keywords: IL17; IL23; coronary artery disease; polymorphisms; psoriasis.
© 2025 The Author(s). Health Science Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1(1):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. PMID: 31917873 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Aug 6;8(8):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub7. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40767824
References
-
- P. A. Nair and T. Badri, “Psoriasis.” Apr 3, 2023. StatPearls [Internet] (Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, 2023 Jan).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

