Dietary niacin intake and epilepsy: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 40809740
- PMCID: PMC12347950
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebr.2025.100814
Dietary niacin intake and epilepsy: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
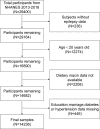
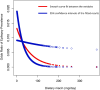
This study aimed to examine the association between dietary niacin intake and the prevalence of epilepsy. We conducted a cross-sectional analysis of 14,236 participants from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2013-2018. Multivariable logistic regression, generalized additive models, and subgroup analyses were employed to assess the relationship. An inverse association was found between dietary niacin intake and the prevalence of epilepsy: for every 10 mg/day increase, the odds of having epilepsy were reduced by 15 % (OR = 0.85, p = 0.0266). Participants in the highest quintile of niacin intake had a significantly lower odds of epilepsy compared to those in the lowest quintile (OR = 0.45, p = 0.0187). This negative association remained consistent across groups with diverse demographic characteristics, medical conditions, and lifestyle choices. Our findings suggest a possible inverse association between dietary niacin intake and the prevalence of epilepsy.
Keywords: Adults; Cross-sectional study; Dietary niacin; Epilepsy; NHANES.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources