Incorporation of oXiris Bioabsorbent Filter into CRRT in the treatment of severe abdominal infections and analysis of associated risk factors for early off-machine
- PMID: 40809760
- PMCID: PMC12343586
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1560587
Incorporation of oXiris Bioabsorbent Filter into CRRT in the treatment of severe abdominal infections and analysis of associated risk factors for early off-machine
Abstract
Introduction: This study aims to evaluate the impact of oXiris continuous renal-replacement therapy (CRRT) on the prognosis of patients with severe intra-abdominal infections (IAIs) and to analyze potential risk factors for early off-machine of oXiris CRRT during treatment.
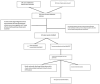
Methods: A total of 49 patients with severe abdominal infections admitted to the intensive care unit of the First Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University from October 2020 to October 2023 were retrospectively analyzed. The patients were divided into a conventional group and an oXiris group. Heart rate, blood lactate level, mean arterial pressure, and total CRRT operation time were observed 72 h before and after CCRT treatment.
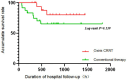
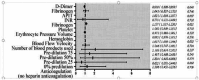
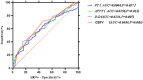
Results: When comparing changes in indicators over the 72-h period between the two groups, no significant difference in survival rate was observed between the two groups. D-dimer [per 1 ng/mL increase, odds ratio (OR) = 0.930, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.866-0.999] was identified as a risk factor for early off-machine. In contrast, prothrombin time (PT, per 1-s increase, OR = 1.117, 95% CI: 1.017-1.226), activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT, per 1-s increase, OR = 1.021, 95% CI: 1.006-1.037), and blood flow velocity (per 1 mL/min increase, OR = 1.027, 95% CI: 1.009-1.046) were found to be protective factors.
Conclusion: oXiris CRRT is associated with a better prognosis in the treatment of severe abdominal infections. APTT, PT, D-dimer, and blood flow velocity are associated with early off-machine during oXiris CRRT.
Keywords: CRRT; early off-machine; oXiris Bioabsorbent Filter; risk factors; severe abdominal infections.
Copyright © 2025 Dong, Chen, Zhang, Wu, Li and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
COMPARISON OF OXIRIS AND CONVENTIONAL CONTINUOUS RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY IN MANAGING SEVERE ABDOMINAL INFECTIONS: IMPACT ON SEPTIC SHOCK MORTALITY.Shock. 2024 Oct 1;62(4):529-538. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000002437. Epub 2024 Aug 14. Shock. 2024. PMID: 39158926
-
Continuous renal replacement therapy with the adsorptive oXiris filter may be associated with the lower 28-day mortality in sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Crit Care. 2023 Jul 9;27(1):275. doi: 10.1186/s13054-023-04555-x. Crit Care. 2023. PMID: 37424026 Free PMC article.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Jun;12(28):iii-iv, ix-95. doi: 10.3310/hta12280. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18547499
-
Reduction Rate of Uric Acid in Blood during Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy for Acute Kidney Injury: A Multicenter Retrospective Observational Study.Blood Purif. 2025;54(2):83-92. doi: 10.1159/000542329. Epub 2024 Oct 29. Blood Purif. 2025. PMID: 39471783 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

