Analysis of the trends in burden of meningitis in China from 1990 to 2021, and projections until 2036
- PMID: 40809770
- PMCID: PMC12343607
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1603244
Analysis of the trends in burden of meningitis in China from 1990 to 2021, and projections until 2036
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to describe the temporal trends in age and sex burdens of meningitis in China from 1990 to 2021 and to compare them with the global burden of the disease.
Methods: Using data from the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) 2021, this study analyzed the features of meningitis burden in China and globally, including incidence, prevalence, mortality, disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), age-standardized incidence rate (ASIR), age-standardized rates of mortality (ASMR), age-standardized rates of prevalence (ASPR), and age-standardized DALY rate (ASDR). The average annual percentage change (AAPC) and associated 95% confidence interval (95% CI) were computed using Joinpoint. A comprehensive comparative analysis of the differences in meningitis burden between China and the world was conducted from multiple dimensions, including age, sex, and periods. Using the BAPC and INLA software tools to perform a Bayesian Age-Period-Cohort (BAPC) analysis in R.
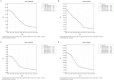
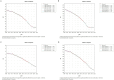
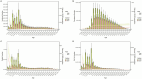
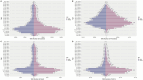
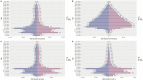
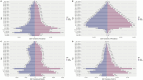
Results: From 1990 to 2021, the ASIR fell from 66.565/100,000 to 31.649/100,000 globally, and from 30.833/100,000 to 5.791/100,000 in China. The ASPR decreased from 11,291,266/100,000 to 92.251/100,000 globally, and from 140.1/100,000 to 16.622/100,000 in China. The ASMR decreased from 7.416/100,000 to 2.947/100,000 globally, while decreased from 3.537/100,000 to 0.475/100,000 in China. The ASDR decreased from 551.176/100,000 to 208.565/100,000 globally, while decreased from 267.304/100,000 to 27.952/100,000 in China. The global AAPC of ASIR, ASPR, ASMR, and ASDR was -2.364, 2.679, -2.970%, and -3.131%, whereas in China it was -5.307, -6.665%, -6.311%, and -7.149, respectively. The effects of age and sex on the burden of meningitis were different. Men had higher incidence and mortality rates of meningitis than women. ASIR in males and females would decrease in the following years.
Conclusion: There was a discernible decline in the incidence, prevalence, mortality, and DALYs associated with meningitis in China and worldwide between 1990 and 2021. Meningitis is more common and fatal in infants and early children, followed by the older adult. Men are more likely than women to die from meningitis and to contract it. It is anticipated that the disease burden of meningitis will continue to decline over the ensuing 12 years. Meningitis continues to be a significant public health concern in China due to the country's huge and aging population.
Keywords: disability-adjusted life years; global burden of disease; incidence; meningitis; mortality; prevalence.
Copyright © 2025 Xu, Xu and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Down syndrome burden in China and globally: a comparative analysis of 1990-2021 trends and future projections based on GBD 2021 database.Front Public Health. 2025 Aug 11;13:1632250. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1632250. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40860557 Free PMC article.
-
Burden of knee osteoarthritis in China and globally: 1990-2045.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025 Jul 1;26(1):582. doi: 10.1186/s12891-025-08858-8. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025. PMID: 40598022 Free PMC article.
-
[Analysis and comparison of the trends in burden of otitis media in China and worldwide from 1992 to 2021].Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2025 Aug 7;60(8):903-910. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115330-20240928-00550. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40890058 Chinese.
-
National and subnational burden of brain and central nervous system cancers in China and global from 1990 to 2021: results from the global burden of disease study 2021.Arch Public Health. 2025 Jul 28;83(1):195. doi: 10.1186/s13690-025-01683-4. Arch Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40722045 Free PMC article.
-
The disease burden of ILD at the global, regional, and national levels from 1990 to 2021, and projections until 2035: the 2021 Global Burden of Disease study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Aug 13;12:1637654. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1637654. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40880770 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

