Tuina Alleviates Neuropathic Pain in CCI Rats by Regulating the TRPV4-CaMKII Signaling Pathway in Dorsal Root Ganglion
- PMID: 40809812
- PMCID: PMC12350020
- DOI: 10.1155/prm/3697374
Tuina Alleviates Neuropathic Pain in CCI Rats by Regulating the TRPV4-CaMKII Signaling Pathway in Dorsal Root Ganglion
Abstract
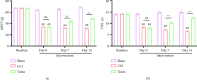
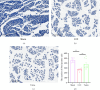
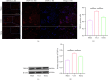
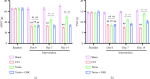
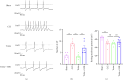
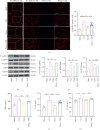
Background: Peripheral sensitization mediated by the Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 4-Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (TRPV4-CaMKII) signaling pathway plays a fundamental role in the generation and maintenance of neuropathic pain (NP). Tuina, a safe and effective therapy in traditional Chinese medicine, shows analgesic effects; however, the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. We aimed to investigate whether Tuina alleviates pain by modulating the TRPV4-CaMKII/CREB/NLRP3 signaling pathway. Methods: The Chronic Constriction Injury (CCI) model of the sciatic nerve was used to simulate clinical NP. Tuina was applied to the Yinmen (BL37), Yanglingquan (GB34), and Chengshan (BL57) acupoints once daily for 14 days. Mechanical Withdrawal Threshold (MWT) and Thermal Withdrawal Latency (TWL) were assessed to evaluate the analgesic effect of Tuina. Its protective effects on dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons were evaluated using Nissl staining. The whole-cell patch clamp technique recorded excitability changes in DRG neurons and assess the effects of Tuina on peripheral sensitization. Western blot (WB), immunofluorescence (IF), and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) helped detect changes in the TRPV4-CaMKII/CREB/NLRP3 pathway and expression of inflammation-related cytokines in DRG neurons. Results: Tuina significantly alleviated mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia in CCI rats and exerted a protective effect on DRG neurons. Patch clamp recordings showed that Tuina inhibited hyperexcitability in DRG neurons. Mechanistically, Tuina downregulated the expression of the TRPV4-CaMKII/CREB/NLRP3 signaling pathway and reduced the secretion of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-18. Conclusion: The analgesic effect of Tuina in CCI rats is associated with reduced peripheral sensitization via modulation of the TRPV4-calcium signaling cascade.
Keywords: TRPV4; Tuina; dorsal root ganglion; neuropathic pain; peripheral sensitization.
Copyright © 2025 Rentuya Na et al. Pain Research and Management published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Van Hecke O., Sophie K. A., Khan R. A., Smith B. H., Torrance N. Neuropathic Pain in the General Population: a Systematic Review of Epidemiological Studies. Pain . 155(4):654–662. - PubMed
-
- Si-Qi W., Zhuo-Ying T., Yang X., Dong-Yuan C. Peripheral Sensitization. In: Turker H., Benavides L. G., Gallardo G. R., del Villar M. M., editors. Peripheral Nerve Disorders and Treatment . London, UK: IntechOpen; 2019. Dec, https://www.intechopen.com/books/peripheral-nerve-disorders-and-treatmen... .
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

