PER1 Serves as a Tumor Suppressor in Breast Cancer by Regulating MEK5/ERK5 Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 40809954
- PMCID: PMC12348893
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S511530
PER1 Serves as a Tumor Suppressor in Breast Cancer by Regulating MEK5/ERK5 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer (BC) is one of the most frequently diagnosed malignant tumors worldwide. Period circadian protein homolog 1 (PER1) is a primary component of the biorhythm molecular oscillation system. The objective of this study was to elucidate the association between PER1 and clinical BC outcomes and determine the potential effect of PER1 on BC tumor development.
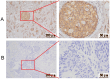
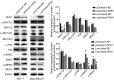
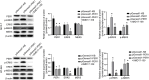
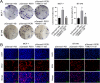
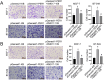
Methods: Immunohistochemical staining for PER1 was performed on 30 normal breast tissue and 172 BC samples. Those BC cases were categorized into two groups to analyze the prognostic significance of PER1 expression. The expression of key proteins in the MEK/ERK pathway (ERK1/2, ERK5, P38, JNK1/2/3) and their phosphorylation levels (p-ERK1/2, p-ERK5, p-P38, and p-JNK1/2/3) were elucidated by western blot test. XMD17-109, a specific ERK5 inhibitor, was used to treat BT-549 and MCF-7 BC cells with knockdown of PER1.
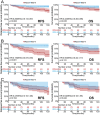
Results: Increased PER1 expression was identified in 26 and 80 normal breast and BC tissues, respectively, whereas low expression was detected in 4 normal and 92 BC tissues. Although no differences were observed in the estrogen receptor (ER), menstrual cycle, TNM, progesterone receptor (PR), and HER-2 stages, age, and tumor size between the two cohorts, both the rate of axillary lymph node metastasis (P<0.05) and vascular tumor thrombosis (P<0.05) were enhanced in the low cohort. Furthermore, the low-PER1 group had the worst overall survival (HR: 0.44, 95% CI: 0.20-0.96, P=0.035) and relapse-free survival (HR: 0.29, 95% CI: 0.13-0.67, P=0.002). PER1 overexpression reduced phosphorylation levels of ERK5 in Lenti-blast-PER1-MDA-MB-231 BC cells (P<0.05), while PER1 silencing had the opposite effect on the pGenesil-1-PER1-MCF-7 cells (P<0.05). Colony formation, 5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine, and Transwell cell migration and invasion assays revealed that XMD17-109 antagonized the enhancement of cell proliferate, migration, and invasion by PER1 knockdown (P<0.05).
Conclusion: PER1 plays an anti-tumor role by regulating the MEK5/ERK5 pathway in BC.
Keywords: MEK5/ERK5; PER1; breast cancer; circadian clock gene; tumor suppressor.
© 2025 Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Upregulated SAE1 Drives Tumorigenesis and Is Associated with Poor Clinical Outcomes in Breast Cancer.Breast J. 2024 Jun 30;2024:2981722. doi: 10.1155/2024/2981722. eCollection 2024. Breast J. 2024. PMID: 39742381 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
-
The Association between ER, PR, HER2, and ER-/PR+ Expression and Lung Cancer Subsequent in Breast Cancer Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study Based on SEER Database.Breast J. 2023 Nov 11;2023:7028189. doi: 10.1155/2023/7028189. eCollection 2023. Breast J. 2023. PMID: 38021219 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dyan B, Seele PP, Skepu A, Mdluli PS, Mosebi S, Sibuyi NRS. A review of the nucleic acid-based lateral flow assay for detection of breast cancer from circulating biomarkers at a point-of-care in low income countries. Diagnostics. 2022;12(8):1973. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12081973 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liang Y, Zhang H, Song X, Yang Q. Metastatic heterogeneity of breast cancer: molecular mechanism and potential therapeutic targets. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020;60:14–27. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

