Efficacy of oral metronomic chemotherapy in the management of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma-a systematic review
- PMID: 40809955
- PMCID: PMC12343508
- DOI: 10.3389/froh.2025.1632316
Efficacy of oral metronomic chemotherapy in the management of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma-a systematic review
Abstract
Background: Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is a group of heterogeneous malignancies and constitutes one of the most prevalent forms of cancer. Oral metronomic chemotherapy (OMCT) is a treatment in which low doses of anticancer drugs are given at regular intervals over a long time, with many advantages over conventional therapies, particularly in nations with high cancer burden. The present systematic review aimed to evaluate the efficacy of OMCT in the management of HNSCC in comparison to other standard chemotherapy regimens. Methodology: The review was registered in the Prospero database (CRD42023426000). An electronic search was conducted using PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science and Google Scholar databases. Articles in which OMCT was used to treat HNSCC were included for systematic review, and the survival and response rates were analyzed.
Results: Twenty-four eligible articles were included for evaluation, which revealed that administration of OMCT produced higher survival and response rates in subjects compared to standard chemotherapy.
Conclusion: The evidence from the included studies supports that oral metronomic chemotherapy is substantially more effective as compared to standard chemotherapy regimens in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/view/CRD42023426000, identifier (CRD42023426000).
Keywords: OSCC (oral squamous cell carcinoma); angiogenesis; head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; oral metronomic chemotherapy; survival rate.
© 2025 Segin Chandran, Pandiar, Krishnan and Gopinath.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
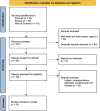
References
-
- Ionna F, Bossi P, Guida A, Alberti A, Muto P, Salzano G, et al. Recurrent/metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: a big and intriguing challenge which may be resolved by integrated treatments combining locoregional and systemic therapies. Cancers (Basel). (2021) 13(10):2371. 10.3390/cancers13102371 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

