Serum uric acid, renal status, cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome and drug therapy, a wide-angled Mendelian randomization analysis
- PMID: 40809993
- PMCID: PMC12344259
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ahjo.2025.100587
Serum uric acid, renal status, cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome and drug therapy, a wide-angled Mendelian randomization analysis
Abstract
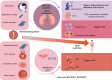
Background: Serum uric acid (SUA) and renal status are associated with the Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic (CKM) syndrome. However, the causal association among them along with drug therapy need to be explored.
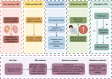
Methods: We employed univariable, multivariate, mediation and drug-target mendelian randomization. Inverse variance weighting was the primary result, with extensive sensitivity analyses conducted to ensure robustness and reliability.
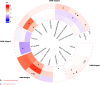
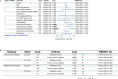
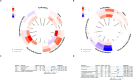
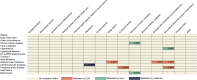
Results: Regarding SUA, genetically predicted SUA demonstrated a potential risk effect on stage 4 of CKM syndrome (ischemic heart disease (IHD), OR = 1.090, 95 %CI: 1.003-1.184; peripheral artery disease, OR = 1.174, 95 %CI: 1.058-1.303). SUA remained a significant risk factor after excluding the confounding of eGFR and proteinuria (IHD: OR = 1.137, 95 %CI: 1.043-1.238; peripheral artery disease: OR = 1.224, 95 %CI: 1.107-1.354). SUA mediated the following causal effect: sleep apnea (2.37 %), income (1.92 %) and education (1.79 %) on IHD; C-reactive protein (11.65 %) and education (4.29 %) on peripheral artery disease. Regarding renal status, renal dysfunction led to a wider phenotype of CKM syndrome including hypertension, cerebrovascular disease, chronic kidney disease and renal failure. Similarly, renal status mediated the causal effect of education on hypertension (1.84 %), depression on cerebrovascular (0.46 %) and family history of diabetes on chronic kidney disease (3.49 %) and renal failure (2.81 %). Lesinurad targeting SLC22A11 and SLC22A12 was validated for treating IHD.
Conclusion: Our study clarified the complex relationship among SUA, renal status and CKM syndrome. Simultaneously providing innovative drug and social interventions for CKM syndrome.
Keywords: Cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome; Mendelian randomization; Renal status; Serum uric acid.
© 2025 Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no relevant conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality: A retrospective cohort study.PLoS Med. 2025 Jun 26;22(6):e1004629. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1004629. eCollection 2025 Jun. PLoS Med. 2025. PMID: 40570007 Free PMC article.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Altered albumin/neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio are associated with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality for advanced cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome.Front Nutr. 2025 Jul 16;12:1595119. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1595119. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40740647 Free PMC article.
-
Blood pressure targets for hypertension in people with chronic renal disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Oct 15;10(10):CD008564. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008564.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39403990
-
Continuous infusion versus bolus injection of loop diuretics for acute heart failure.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 May 22;5(5):CD014811. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014811.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38775253 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ndumele C.E., Neeland I.J., Tuttle K.R., et al. A synopsis of the evidence for the science and clinical Management of Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic (CKM) syndrome: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2023;148(20):1636–1664. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001186. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Khan S.S., Coresh J., Pencina M.J., et al. Novel prediction equations for absolute risk assessment of Total cardiovascular disease incorporating cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic health: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2023;148(24):1982–2004. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001191. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dawson J., Quinn T., Walters M. Uric acid reduction: a new paradigm in the management of cardiovascular risk? Curr. Med. Chem. 2007;14(17):1879–1886. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

