Wedelolactone Ameliorates Ischemic Stroke by Inhibiting Oxidative Damage and Ferroptosis via HIF-1α/SLC7A11/GPX4 Signaling
- PMID: 40810078
- PMCID: PMC12345358
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S528831
Wedelolactone Ameliorates Ischemic Stroke by Inhibiting Oxidative Damage and Ferroptosis via HIF-1α/SLC7A11/GPX4 Signaling
Abstract
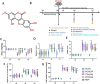
Purpose: Wedelolactone (Wel), a furocoumarin compound extracted from the medicinal plant Eclipta prostrata L. has been shown to exhibit significant neuroprotective effects. However, the potential of Wel to improve ischemic stroke (IS) and the underlying mechanisms remain unclear.
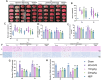
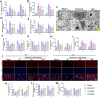
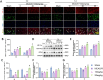
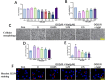
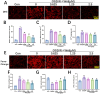
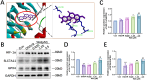
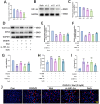
Methods: The middle cerebral artery occlusion and reperfusion (MCAO/R) and oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation (OGD/R) were established to evaluate the potential neuroprotective of Wel. Neurological function, brain infarct volume, brain swelling, and histopathological staining were analyzed to demonstrate the therapeutic efficacy of Wel. The occurrence of ferroptosis was confirmed by quantifying the levels of ROS and Fe2+, and by examining the ultrastructural features of cells. The binding affinity between Wel and HIF-1α was evaluated using Molecular docking. Immunofluorescence and Western blot analyses were conducted to explore the regulation of Wel on the HIF-1α/SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway. Finally, the expression of HIF-1α was down-regulated to verify whether Wel exerts neuroprotection by modulating HIF-1α to inhibit ferroptosis of cells.
Results: The results demonstrated that Wel effectively inhibit neuron ferroptosis after MCAO/R in a dose-time-dependent manner, thereby alleviating brain injury. Moreover, at the cellular level, Wel significantly reduced the accumulation of Fe2+ and ROS after OGD/R. Further investigation revealed that Wel might inhibit neuronal ferroptosis and improve IS by promoting the nuclear translocation and accumulation of HIF-1α, subsequently regulating the expression of downstream proteins SLC7A11 and GPX4. Notably, the inhibitory effect of Wel on ferroptosis was markedly attenuated by HIF- 1α siRNA in OGD/R PC12 cells.
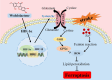
Conclusion: Our discovery revealed that the Wel could alleviate IS by inhibiting oxidative damage and ferroptosis via HIF-1α/ SLC7A11/GPX4 signaling pathway. Wel may represent a promising active compound for anti-IS, while also providing novel insights into the elucidation of its molecular mechanisms and potential clinical implications.
Keywords: HIF-1α/SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway; Wedelolactone; ferroptosis; ischemic stroke.
© 2025 Tao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective effects of Rosavin via HIF-1α signaling in a rat model of ischemic stroke.Phytomedicine. 2025 Sep;145:157068. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.157068. Epub 2025 Jul 13. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40682944
-
Protecting the brain from stroke: Huoxue Rongluo formula (HXRLF) targets ferroptosis for neuroprotection.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jul 29;353(Pt A):120329. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.120329. Online ahead of print. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40744419
-
Remote Ischemic Postconditioning Improve Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Induced Cognitive Dysfunction through Suppressing Mitochondrial Apoptosis in Hippocampus via TK/BK/B2R-Mediated PI3K/AKT.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Aug;62(8):10652-10669. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04864-y. Epub 2025 Apr 14. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40229456 Free PMC article.
-
Dimethyl malonate preserves brain and neurobehavioral phenotype following neonatal hypoxia-ischemia by inhibiting FTH1-mediated ferritinophagy.Redox Biol. 2025 Jul 29;86:103792. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2025.103792. Online ahead of print. Redox Biol. 2025. PMID: 40749519 Free PMC article.
-
Nature's answer to Ferroptosis: how bioactive compounds rewire oxidative stress circuits in cerebral ischemia.Int Immunopharmacol. 2025 Jul 23;163:115250. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.115250. Online ahead of print. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40706206 Review.
