Metabolic Reprogramming-Related Genes in Lung Adenocarcinoma: Identification and Prognostic Model Construction
- PMID: 40810083
- PMCID: PMC12339286
- DOI: 10.14740/wjon2604
Metabolic Reprogramming-Related Genes in Lung Adenocarcinoma: Identification and Prognostic Model Construction
Abstract
Background: Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD), the predominant histological subtype of lung cancer, persists in presenting a dismally low 5-year overall survival (OS) rate, notwithstanding advancements in treatment modalities. There exists a pressing necessity for the identification of innovative biomarkers that can enhance prognostic assessments and facilitate individualized therapeutic strategies. The objective of this investigation was to clarify the involvement of genes associated with metabolic reprogramming in the progression of LUAD and to evaluate their viability as prognostic indicators.
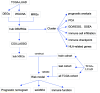
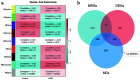
Methods: An analysis of differential gene expression was performed utilizing The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA)-LUAD dataset, supplemented by a weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA). Through intersection analysis focusing on metabolic reprogramming genes (MRGs), pivotal differentially expressed metabolic reprogramming genes (hub DEMRGs) were identified. Consensus clustering categorized patients into subtypes based on these genes. Functional enrichment analysis and immune microenvironment characterization were conducted, followed by Cox and least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression analyses to construct a prognostic risk model.
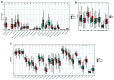
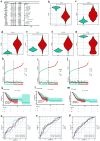
Results: A total of 31 hub DEMRGs were identified. Patients were classified into two distinct subtypes (C1 and C2), with the C2 subtype exhibiting a markedly reduced OS rate. Functional enrichment revealed significant activation of nuclear division and cell cycle pathways in C2. Immune profiling demonstrated an immunosuppressive phenotype in C2, characterized by elevated M2 macrophage infiltration and reduced CD8+ T cells. The risk model based on five critical hub DEMRGs showed robust predictive performance (area under the curve (AUC): 0.68 - 0.71), and high-risk patients displayed unique immune cell infiltration patterns.
Conclusions: This research highlights the critical role of MRGs in LUAD prognosis and their potential for clinical application. The identified subtypes and risk model provide insights into tumor heterogeneity and immunosuppressive mechanisms, offering potential targets for individualized therapy.
Keywords: Consensus clustering; Lung adenocarcinoma; Metabolic reprogramming genes; Prognostic model; Weighted gene co-expression network analysis.
Copyright 2025 Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Unraveling the role of GPCR signaling in metabolic reprogramming and immune microenvironment of lung adenocarcinoma: a multi-omics study with experimental validation.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 6;16:1606125. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1606125. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40547013 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular subtypes of lung adenocarcinoma patients for prognosis and therapeutic response prediction with machine learning on 13 programmed cell death patterns.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Oct;149(13):11351-11368. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05000-w. Epub 2023 Jun 28. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37378675 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular sub-type and the development and validation of a prognosis prediction model based on endocytosis-related genes for hepatocellular carcinoma.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025 Jun 30;16(3):1115-1126. doi: 10.21037/jgo-2025-359. Epub 2025 Jun 27. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40672080 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and validation of a lipid metabolism-related genes prognostic signature for skin cutaneous melanoma.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2025 Aug 15;775:152115. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2025.152115. Epub 2025 May 29. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2025. PMID: 40460484
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
References
-
- Travis WD, Brambilla E, Nicholson AG, Yatabe Y, Austin JHM, Beasley MB, Chirieac LR. et al. The 2015 World Health Organization Classification of Lung Tumors: impact of genetic, clinical and radiologic advances since the 2004 classification. J Thorac Oncol. 2015;10(9):1243–1260. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000630. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
