Traditional Chinese herbal medicine Qingre Xiaozheng formula improves renal outcomes in patients with diabetic kidney disease: a retrospective study
- PMID: 40810234
- PMCID: PMC12340587
- DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.04.017
Traditional Chinese herbal medicine Qingre Xiaozheng formula improves renal outcomes in patients with diabetic kidney disease: a retrospective study
Abstract
Objective: To assess the benefits of Qingre Xiaozheng formula (, QRXZF) as an adjunct to standard Western medical management on renal outcomes in patients with diabetic kidney disease (DKD).
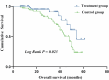
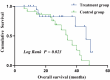
Methods: This retrospective study included patients with DKD who received the QRXZF between May 2017 and May 2021. A total of 144 patients with DKD, 24 h urinary total protein (24 h-UTP) ≥ 0.5 g, and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) ≥ 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2 were divided into the treatment group or the control group based on whether they received QRXZF treatment. The long-term renal outcomes of patients with DKD were analyzed to evaluate the effectiveness of the QRXZF. Differences in overall survival (OS) were assessed using Kaplan-Meier curve analysis. Cox proportional hazards regression analysis was used to determine the independent risk factors for renal endpoints.
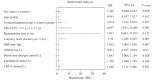
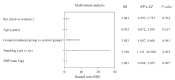
Results: The mean follow-up period was (28±15) months. Nine (12.5%) patients in the treatment group and 27 (37.5%) patients in the control group met the renal endpoints. Multivariate Cox regression analysis showed that 24 h-UTP ≥ 3.5 g [hazard ratio (HR) = 4.70, 95% confidence interval (CI) (1.83, 12.05), P = 0.001], combined coronary artery disease [HR = 3.39, 95% CI (1.65, 6.98), P = 0.001], total cholesterol [HR = 1.34, 95% CI (1.05, 1.70), P = 0.019] and low-density lipoprotein [HR = 1.65, 95% CI (1.111, 2.45), P = 0.013] were independent prognostic factors for renal endpoints in patients with DKD. Compared with the treatment group, the risk of renal endpoint events increased 2.68-fold in the control group [HR = 2.68, 95% CI (1.19, 6.02); P = 0.017]. We included 48 patients with 24 h-UTP ≥ 3.5 g in a further stratification analysis of patients with DKD. The independent risk factor for the renal endpoints in patients with 24h-UTP ≥ 3.5 g was smoking history [HR = 5.52, 95% CI (1.131, 26.92), P = 0.035]. Compared with the treatment group, the risk of renal endpoint events increased 3.01-fold in the control group [HR = 3.01, 95% CI (1.05, 8.67); P = 0.041].
Conclusions: The results show that QRXZF treatment improved renal outcomes and reduced proteinuria in patients with DKD. These results indicate that Traditional Chinese Medicine is likely to have a positive therapeutic effect on established and advanced DKD. Further well-designed clinical trials with longer follow-up periods are required.
Keywords: Qingre Xiaozheng formula; diabetic nephropathies; renal outcome; retrospective studies.
Figures
References
-
- Zhang L, Long J, Jiang W, et al. . Trends in chronic kidney disease in China. N Engl J Med 2016; 375: 905-6. - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association 11. Microvascular complications and foot care: standards of medical care in diabetes-2021. . Diabetes care 2021; 44: S151-67. - PubMed
-
- Miyamoto S, Heerspink HJL, de Zeeuw D, et al. . A randomized, open-label, clinical trial examined the effects of canagliflozin on albuminuria and eGFR decline using an individual pre-intervention eGFR slope. Kidney Int 2024; 106: 972-84. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
