Conditional neuronal deletion of microRNA-141/200c cluster, but not microRNA-181a/b-1 cluster, is protective against experimental stroke in male mice
- PMID: 40810631
- PMCID: PMC12351801
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.70505
Conditional neuronal deletion of microRNA-141/200c cluster, but not microRNA-181a/b-1 cluster, is protective against experimental stroke in male mice
Abstract
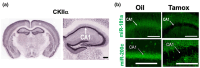
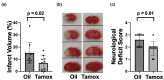
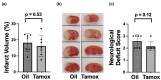
MicroRNAs (miRs) regulate the translation of target genes often in a cell-type specific manner. We previously demonstrated that downregulation of either miR-181a or miR-200c with intracranial injection of an inhibitor is protective against experimental stroke in mice. Here, we generated genetic lines of inducible Ca2+-calmodulin kinase IIα (CKIIα) neuronal miR-181a/b-1 and miR-141/200c cluster deletion to investigate whether the protective effect of their inhibition could be neuron-specific. Jackson Lab strains Mirc14tm1.1Czc/J and Mirc13tm1Mtm/Mmjax were each crossed with the tamoxifen-inducible Cre-recombinase strain B6;129S6-Tg, CKIIα-cre/ERT2. Adult double transgenic male mice were randomized and treated with 3 mg tamoxifen or vehicle via oral gavage for 7 days prior to 1 h middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) or sham surgery. Mice were assessed for gross motor function at 24 h and then sacrificed for quantification of infarct volume. Separate animals were assessed for cell-type specific brain expression of miR-181a and miR-200c via combined fluorescent immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization. Brains from tamoxifen treated mice exhibited selective miR deletion in CKIIα neurons. Infarct volumes were significantly lower, and neurological scores significantly improved in CKIIα/miR-200c mice pretreated with tamoxifen versus vehicle alone. In contrast, no difference was observed in infarct volume or neurological score in CKIIα/miR-181a mice pretreated with tamoxifen versus vehicle.
Keywords: CKIIα; MCAO; cell type; miR; miRNA.
© 2025 The Author(s). Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Antiretrovirals for reducing the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jan 24;(1):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Jul 06;(7):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub3. PMID: 17253490 Updated.
-
Antiretrovirals for reducing the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Jul 6;(7):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. PMID: 21735394
-
Clomiphene and other antioestrogens for ovulation induction in polycystic ovarian syndrome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Dec 15;12(12):CD002249. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002249.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27976369 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
References
-
- Arvola, O. , Kaidonis, G. , Xu, L. , Griffiths, B. , & Stary, C. M. (2019). Hippocampal sub‐regional differences in the microRNA response to forebrain ischemia. Molecular and Cellular Neurosciences, 98, 164–178. - PubMed
-
- Attwell, D. , & Laughlin, S. B. (2001). An energy budget for signaling in the grey matter of the brain. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 21(10), 1133–1145. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

