Stress granule-mediated ZBP1 activation drives necroptotic cell death in non-obstructive azoospermia and testicular aging
- PMID: 40811463
- PMCID: PMC12377765
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2514837122
Stress granule-mediated ZBP1 activation drives necroptotic cell death in non-obstructive azoospermia and testicular aging
Abstract
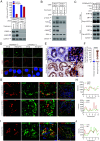
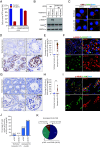
Male infertility remains a major unmet medical challenge, with poorly defined molecular mechanisms and no effective therapies. Here, we identify a stress granule-mediated necroptotic pathway as a key driver of non-obstructive azoospermia, a severe form of male infertility marked by the loss of spermatogenesis. Environmental or physiological stress activates eIF2α kinases, inducing stress granule formation and the recruitment of ZBP1 and RIPK3 into a cytoplasmic complex. This assembly triggers RIPK3 activation, MLKL phosphorylation, and necroptotic death of spermatogonia and Sertoli cells. Genetic ablation of Zbp1 or Ripk3 protects mice from heat-induced testicular degeneration, establishing their essential role in stress-induced testicular damage. Importantly, activation of this pathway is also observed in aged human testes, linking stress-responsive necroptosis to both pathological infertility and the broader process of reproductive aging. These findings reveal an unrecognized mechanism that couples cellular stress responses to regulated cell death in the male reproductive system.
Keywords: ZBP1; necroptosis; non-obstructive azoospermia; stress granule; testis aging.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:Xiaodong Wang is the co-founder of Sironax Inc., a biotech start-up developing therapeutic agents for degenerative diseases, Xiaodong Wang own 5.5% of Sironax stock.
Figures



References
-
- McLachlan R. I., Rajpert-De Meyts E., Hoei-Hansen C. E., de Kretser D. M., Skakkebaek N. E., Histological evaluation of the human testis–approaches to optimizing the clinical value of the assessment: Mini review. Hum. Reprod. 22, 10 (2007). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

