Neurodevelopmental disorder mutations in the exchange factor DENN/MADD disrupt activation of Rab GTPases
- PMID: 40812422
- PMCID: PMC12495445
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.110588
Neurodevelopmental disorder mutations in the exchange factor DENN/MADD disrupt activation of Rab GTPases
Abstract
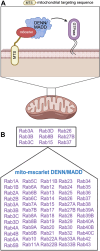
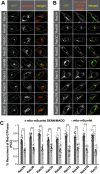
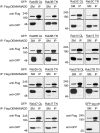
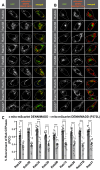
DENN/MADD (mitogen-activated protein kinase-activating death domain), a differentially expressed in normal and neoplastic cells (DENN) domain-containing protein functions in membrane trafficking. DENN domain-bearing proteins have guanine nucleotide exchange factor activity toward Rab GTPases. Here, we identify Rab GTPase substrates for DENN/MADD using a cell-based assay involving DENN domain-mediated recruitment of Rab substrates to mitochondria. We confirmed known interactions of DENN/MADD with Rab3A, Rab3B, Rab3C, Rab3D, and Rab27B and identified four new potential substrates, Rab8B, Rab15, Rab26, and Rab37, results confirmed with biochemical experiments. Mutations in the DENN domain of DENN/MADD result in diverse pathophysiological manifestations, ranging from predominant neurological dysfunction to a multisystem disorder. Structural analysis using AlphaFold suggested that these mutations affect DENN/MADD's interaction with Rab GTPases. Introducing such mutations into DENN/MADD's DENN domain influenced the mitochondrial recruitment of Rabs. This study identifies new DENN/MADD protein interactions and cellular pathways, the disruption of which results in human disorders.
Keywords: DENN/MADD; Rab GTPases; cell biology; genetic disease; guanine nucleotide exchange factor; imaging; membrane trafficking; neurodevelopmental disorder; protein–protein interaction.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

