Using ultrasound to define inflammatory and non-inflammatory phenotypes in difficult-to-treat psoriatic arthritis
- PMID: 40813109
- PMCID: PMC12352194
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2025-005785
Using ultrasound to define inflammatory and non-inflammatory phenotypes in difficult-to-treat psoriatic arthritis
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the prevalence of difficult-to-treat psoriatic arthritis (D2T-PsA) and classify patients with persistent inflammatory PsA (PIPsA) and non-inflammatory PsA (NIPsA) based on a combination of clinical and musculoskeletal ultrasound (MSUS) evidence of inflammation.
Methods: A multicentre cross-sectional study was conducted on PsA patients treated with biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs/targeted synthetic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (b/tsDMARDs). D2T-PsA status was characterised by an inadequate response to ≥2 classes of b/tsDMARDs and the persistence of active disease, defined as a DAPSA >14.
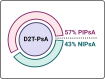
Results: Out of 517 PsA patients on b/tsDMARDs, 53 (10.3%) met the criteria for D2T-PsA with 30 (57%) classified as PIPsA and 23 (43%) classified as NIPsA. The PIPsA phenotype had higher swollen joint count (2.5 (IQR 1.0-7.0) vs 0.0 (IQR 0.0-1.0), p<0.001), dactylitis (20% vs 0%, p=0.030) and nail psoriasis (40% vs 13%, p=0.027). Conversely, NIPsA patients had significantly greater ΔPtGA-PhGA (4.0 (IQR 2.5-5.0) vs 0.0 (IQR 0.0-1.5), p<0.001), higher tender points (16.0 (IQR 0.0-18.0) vs 0.0 (IQR 0.0-8.0), p=0.009), a higher SPARCC enthesitis index (5.0 (IQR 2.0-8.0) vs 2.0 (IQR 0.0-5.0), p=0.023). The MSUS showed higher ultrasound activity (3.81±2.0 vs 0.91±0.5, p<0.001) and greater structural damage (4.12±1.0 vs 2.38±2.1, p<0.001), with both activity and damage scores being higher in PIPsA patients.
Conclusion: The classification into PIPsA and NIPsA based on easily detectable clinical features can support a tailored therapeutic management of patients with D2T-PsA.
Keywords: Arthritis, Psoriatic; Inflammation; Pain; Ultrasonography.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
