Sustainable UV approaches backed by one step extraction procedure for quantifying the newly released mirabegron and silodosin mixture in urine
- PMID: 40813404
- PMCID: PMC12354732
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-13989-y
Sustainable UV approaches backed by one step extraction procedure for quantifying the newly released mirabegron and silodosin mixture in urine
Abstract
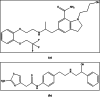
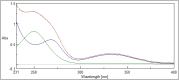
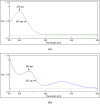
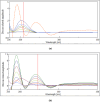
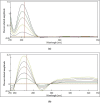
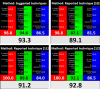
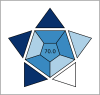
Mirabegron (MIR) and silodosin (SIL) have recently been combined in a single pill to significantly enhance the effectiveness of treating detrusor hyperactivity with impaired contractility (DHIC), leading to appreciable improvements in symptoms associated with overactive bladder. Additionally, this combination effectively manages lower ureteric stones and improves patient outcomes with no significant side effects, especially in elderly patients. Accordingly, this study introduces two UV techniques for analyzing MIR and SIL in their mixtures (pure and commercial mixtures). These techniques were backed by a one-step salting-out liquid/liquid extraction (SALLE) procedure for quantifying MIR and SIL in urine samples without matrix interference. The proposed UV techniques succeeded in resolving the superimposed MIR's and SIL's UV spectra by employing straightforward mathematical filtration. The UV techniques were Fourier self-deconvolution (FSD) and induced dual-wavelength (IDW) techniques, with linearities of (50-350) µg/mL for MIR and (5-100) µg/mL for SIL. The applied techniques were verified following the International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) directives and were statistically evaluated against the published technique, with no noteworthy differences found. The applied techniques' practicality (blueness), whiteness, and greenness were appraised utilizing various metrics. Per the preceding, the applied approaches have been proven to be sustainable, delicate, and appropriate for quality control (QC) testing. Also, backing the applied approaches with the SALLE procedure enables precise monitoring of MIR and SIL in miscellaneous biological fluids with excellent recoveries, presenting an inventive approach for further bioanalytical applications.
Keywords: Fourier self-deconvolution; Induced dual-wavelength; Mirabegron; SALLE; Silodosin.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Safety and efficacy of an α1 -blocker plus mirabegron compared with an α1 -blocker plus antimuscarinic in men with lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia and overactive bladder: A systematic review and network meta-analysis.Neurourol Urodyn. 2024 Mar;43(3):604-619. doi: 10.1002/nau.25399. Epub 2024 Jan 30. Neurourol Urodyn. 2024. PMID: 38291827
-
Comparative Safety and Efficacy of Treatments for Overactive Bladder Among Older Adults: A Network Meta-analysis.Drugs Aging. 2020 Nov;37(11):801-816. doi: 10.1007/s40266-020-00792-9. Drugs Aging. 2020. PMID: 32960422 Free PMC article.
-
Invasive urodynamic investigations in the management of women with refractory overactive bladder symptoms: FUTURE, a superiority RCT and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2025 Jul;29(27):1-139. doi: 10.3310/UKYW4923. Health Technol Assess. 2025. PMID: 40620147 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
References
-
- Chughtai, B. et al. Benign prostatic hyperplasia. Nat. Reviews Disease Primers2, 1–15 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Seipel, T. & Schauss, A. G. Lower urinary tract symptoms, overactive bladder syndrome, and urinary incontinence (LUTS, OAB, and UI), textbook of natural medicine. 1533–1544. (2020).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

