A graph attention network-based multi-agent reinforcement learning framework for robust detection of smart contract vulnerabilities
- PMID: 40813415
- PMCID: PMC12354882
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-14032-w
A graph attention network-based multi-agent reinforcement learning framework for robust detection of smart contract vulnerabilities
Abstract
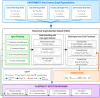
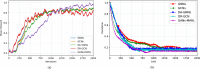
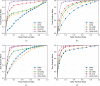
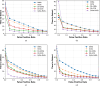
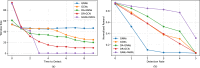
Smart contracts have revolutionized decentralized applications by automating agreement enforcement on blockchain platforms. However, detecting vulnerabilities in smart contract interactions remains challenging due to complex state interdependencies. This paper presents a novel approach using multi-agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) to identify smart contract vulnerabilities. We integrate a Hierarchical Graph Attention Network (HGAT) into a Multi-Agent Actor-Critic framework, decomposing vulnerability detection into complementary policies: a high-level policy encoding historical interactions and a low-level policy capturing structured actions within contract state spaces. By modeling interactions as multistep reasoning paths, our MARL framework effectively navigates complex transaction sequences and resolves semantic ambiguities across different contract states. Experimental evaluations on real-world blockchain datasets demonstrate significant improvements in detecting multiple vulnerability types. For reentrancy attacks, our model achieves 93.8% accuracy and an 89.8% F1 score. The framework also performs strongly in detecting front running (88.9% accuracy), denial-of-service attacks (91.2% accuracy), and unchecked low-level vulnerabilities (91.6% accuracy), outperforming existing approaches across all vulnerability categories.
Keywords: Blockchain vulnerability detection; Decentralized application; Graph attention networks; Hierarchical reinforcement learning; Predictive analytics; Smart contract security.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Nakamoto, S. Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System. Bitcoin.org Whitepaper (2008). Available online: https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf.
-
- Wood, G. et al. Ethereum: A secure decentralised generalised transaction ledger. Ethereum Project Yellow Paper151, 1–32 (2014).
-
- Buterin, V. Ethereum: A next-generation smart contract and decentralized application platform. Ethereum White Paper3, 2–1 (2013).
-
- FBI, Internet Crimes Complaint Center (IC3) Cyber criminals increasingly exploit vulnerabilities in decentralized finance platforms to obtain cryptocurrency, causing investors to lose money (2022). I-082922-PSA.
-
- Lai, E. & Luo, W. Static analysis of integer overflow of smart contracts in ethereum. In Proceedings of the 2020 4th International Conference on Cryptography, Security and Privacy, 110–115 (2020).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

