Genetic background and oncogenic driver determines the genomic evolution and transcriptomics of mammary tumor metastasis
- PMID: 40813609
- PMCID: PMC12354892
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-025-08624-5
Genetic background and oncogenic driver determines the genomic evolution and transcriptomics of mammary tumor metastasis
Abstract
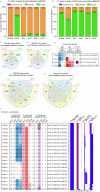
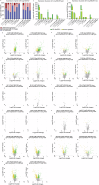
Metastasis remains a major cause of cancer mortality. This study, expanding upon previous findings in the MMTV-PyMT model, investigated four independent mouse models, representing luminal (MMTV-PyMT, MMTV-Myc), HER2-amplified (MMTV-Her2), and triple-negative (C3(1)TAg) breast cancer subtypes. Consistent with previous results, limited evidence for metastasis-associated somatic point mutations was found for all models. We also found that oncogenic drivers significantly influenced the number and size of metastasis-specific copy number variations (MSCNVs), but common driver-independent MSCNVs were rare. Furthermore, analyzing a cohort with varying genetic backgrounds while maintaining a constant oncogenic driver (PyMT) revealed that genetic background profoundly impacts MSCNVs. Transcriptome analysis demonstrated that oncogenic drivers strongly shaped metastasis-specific gene expression (MSGE), with each driver exhibiting distinct expression profiles. In contrast, MSGE in the PyMT-F1 cohort was more variable across strains. Despite the diversity of MSCNV and MSGE, functional analysis revealed that both mechanisms converge on the modulation of key cellular processes, including immune responses, metabolism, and extracellular matrix interactions. These findings emphasize the complex interplay between oncogenic drivers and genetic background in shaping the genomic and transcriptional landscapes of metastatic lesions.
© 2025. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Contributions of the RhoA guanine nucleotide exchange factor Net1 to polyoma middle T antigen-mediated mammary gland tumorigenesis and metastasis.Breast Cancer Res. 2018 May 16;20(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s13058-018-0966-2. Breast Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29769144 Free PMC article.
-
Distinctive chromosomal, mutational and transcriptional profiling in colon versus rectal cancers.J Transl Med. 2025 Aug 6;23(1):869. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06908-2. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40770356 Free PMC article.
-
Short-term consumption of the modified standard American diet perturbed the metabolic balance and altered DNA damage in MMTV-PyMT transgenic mice.Breast Cancer Res. 2025 Jul 25;27(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s13058-025-02075-w. Breast Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40713647 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program (www.seer.cancer.gov) SEER*Stat Database: Mortality - All COD, Aggregated With State, Total U.S. (1969-2023), National Cancer Institute, DCCPS, Surveillance Research Program, released February 2025. Underlying mortality data provided by NCHS (www.cdc.gov/nchs)
-
- Nowell, P. C. The clonal evolution of tumor cell populations. Science194, 23–28 (1976). - PubMed
-
- Dasari, S. et al. Genomic attributes of prostate cancer across primary and metastatic noncastrate and castrate resistant disease states: a next generation sequencing study of 183 patients. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis.28, 506–508 (2025). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

