Use of modern family planning methods and its association with quality of life among Rwandan women: a multi-center cross-sectional study
- PMID: 40813710
- PMCID: PMC12355850
- DOI: 10.1186/s40834-025-00374-3
Use of modern family planning methods and its association with quality of life among Rwandan women: a multi-center cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: Family planning (FP) promotes sustainable population growth and enhances societal well-being. Despite its recognized importance, the quality of life (QoL) of women utilizing modern FP methods in Rwanda remains underexplored. Women's experiences and perceptions of contraceptive methods significantly influence their uptake and continued use.
Objective: This study aimed to assess the QoL of women using modern FP methods in Rwanda.
Methodology: A multicenter cross-sectional study was conducted involving 415 women who had been using modern FP methods for at least six months. Participants were recruited from the University Teaching Hospital of Kigali (CHUK) and four selected Health Centers in Rwanda. The Short-Form 36 (SF-36) Health Survey was used to evaluate the QoL. Data analysis was performed using the R programming version 4.0.2.
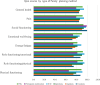
Results: Participants reported overall favorable QoL across all domains. Social functioning scored the highest (94.16%, SD = 17), while physical functioning scored the lowest (80.6%, SD = 34.45). Women aged 32-38 had significantly higher QoL scores in role functioning, including social functioning, role functioning due to physical issues, and role functioning due to emotional issues (p < 0.001, p = 0.014, and p = 0.034, respectively). The type of FP Method was strongly associated with QoL outcomes in all domains, with Intrauterine Devices (IUDs) correlating with the highest scores, particularly in physical functioning (p < 0.001). Rural women reported better general health (p < 0.001) compared to their urban counterparts.
Conclusion: Women using modern FP methods in Rwanda generally reported a high QoL. Both the FP method type and age significantly influenced QoL outcomes. Thus, there is a need to promote the universal use of Modern FP methods among women of reproductive age in Rwanda.
Keywords: Contraceptive methods; Modern family planning; Quality of Life (QoL); Reproductive health; Rwanda; Women's health.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The ethical Clearance was obtained from the Institutional Review Board, College of Medicine and Health Science (IRB/CMHS) at the University of Rwanda and CHUK with Approval number: 189/CMHS IRB/2022. Consent forms were obtained from participants before the study. Consent for publication: Not Applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Behavioral interventions for improving contraceptive use among women living with HIV.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Aug 9;2016(8):CD010243. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010243.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27505053 Free PMC article.
-
Inequality in modern contraceptive use and unmet need for contraception among women of reproductive age in Zambia. A trend and decomposition analysis 2007-2018.Reprod Health. 2024 Dec 9;21(1):181. doi: 10.1186/s12978-024-01909-8. Reprod Health. 2024. PMID: 39654062 Free PMC article.
-
Oral health-related quality of life among people living with HIV and HIV-negative adults in Kigali, Rwanda: a comparative cross-sectional study.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Jan 25;24(1):128. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03828-9. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 38273293 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral interventions for improving contraceptive use among women living with HIV.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jan 31;(1):CD010243. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010243.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Aug 09;(8):CD010243. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010243.pub3. PMID: 23440846 Updated.
References
-
- Family planning/contraception methods. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/family-planning-contrac.... Accessed 23 Aug 2024.
-
- Ertekin Pinar S, Demirel G, Yildirim G, Daglar G. Sexual experiences and quality of life in Turkish women using methods of contraception. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2019;39(6):782–7. 10.1080/01443615.2019.1581738. - PubMed
-
- WHOQOL - Measuring quality of life| The World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/tools/whoqol. Accessed 23 Aug 2024.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous