TRP channels and cancer modulation: a voyage beyond metabolic reprogramming, oxidative stress and the advent of nanotechnologies in targeted therapy
- PMID: 40813985
- PMCID: PMC12351952
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-025-03495-4
TRP channels and cancer modulation: a voyage beyond metabolic reprogramming, oxidative stress and the advent of nanotechnologies in targeted therapy
Abstract
Transient receptor potential (TRP) channels are a large family of non-selective cation channels that play critical roles in cellular homeostasis and signal transduction. Recent investigations have clearly highlighted their involvement in cancer biology, particularly in the regulation of cancer metabolism. Unlike normal cells, cancer cells tend to favour the energy inefficient glycolytic pathway over the more effective oxidative phosphorylation process. TRP channels are involved in critical steps of cancer-related metabolic reprogramming by influencing intracellular Ca2+ signaling. Their dysregulation can intensify oxidative stress, thereby promoting oncogenic transformation and tumor progression. The intricate interplay between TRP channels, metabolic reprogramming and oxidative stress promotes cancer cell progression and resistance to treatment. This review highlights the crucial role of TRP channels in tumorigenesis. It examines how TRPM7 and TRPM8 contribute to metabolic reprogramming by its involvement in glycolysis pathway. Additionally, it explores the involvement of TRPML1, TRPA1, TRPM2, and TRPV1 in modulating reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels within cancer cells, analyzing the ROS dual role in tumor modulation. The advent of nanotechnology, particularly through the utilisation of engineered nanoparticles, has facilitated the selective modulation of TRPA1, TRPM2, and TRPV1 channels. This technological breakthrough has paved the way for novel and more targeted anticancer treatment strategies. The integration of molecular insights with cutting-edge technological approaches holds great promise for the development of more effective and targeted cancer treatments.
Keywords: Cancer; Metabolic reprogramming; Nanotechnologies; Oxidative stress; TRP channels.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not required for this study. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
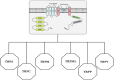

References
-
- Zou J, Wang E. Cancer biomarker discovery for precision medicine: new progress. Curr Med Chem. 2020;26:7655–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

