Elevated TIM3 expression on bone marrow T cells drives immune dysfunction in early relapsed blood cancer after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
- PMID: 40814113
- PMCID: PMC12355862
- DOI: 10.1186/s40164-025-00697-6
Elevated TIM3 expression on bone marrow T cells drives immune dysfunction in early relapsed blood cancer after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Abstract
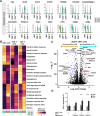
Relapse after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) remains the leading cause of treatment failure in patients with hematologic malignancies. To better understand the mechanisms underlying early relapse (ER), we comprehensively explored the expression of inhibitory receptors (IRs) in bone marrow (BM) T cells at differentiation stage and examined transcriptional differences. Among the evaluated IRs, TIM3 was significantly upregulated in CD3+T cells of patients with ER compared to patients with complete remission (CR). Notably, double-negative T (DNT) cells, a unique subset with MHC-independent cytotoxic potential, constituted a high proportion of BM T cells and expressed increased TIM3 expression in ER patients. Moreover, regulatory T cells (Tregs) showed elevated TIM3 levels, contributing to an immunosuppressive microenvironment after allo-HSCT. Transcriptomic analysis revealed downregulation of cytotoxic granules and effector genes in DNT cells from ER patients. Functional assays demonstrated that TIM3 blockade with sabatolimab restored T cell cytotoxicity, leading to enhanced leukemia cell apoptosis in ER patients. These findings highlight TIM3 as a critical regulator of T cell exhaustion and immune suppression in patients with ER and provide a rationale for the therapeutic use of TIM3 blockade in preventing and treating relapses after allo-HSCT.
Keywords: Allogeneic hematologic stem cell transplantation (HSCT); Double negative t cells (DNTs); Early relapse (ER); Inhibitor receptors; Leukemia immune microenvironment; Regulatory t cells (Treg); Sabatolimab; T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 3 (TIM3).
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval and consent to participate: The study protocol has been developed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Chungnam National University Hospital (IRB number: 2018-02-032-014). Written informed consent was obtained from all patients. Consent for publication: All the authors agree to publish. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Kreidieh F, Abou Dalle I, Moukalled N, El-Cheikh J, Brissot E, Mohty M, et al. Relapse after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in acute myeloid leukemia: an overview of prevention and treatment. Int J Hematol. 2022;116(3):330–40. - PubMed
-
- Merryman RW, Armand P. Immune checkpoint Blockade and hematopoietic stem cell transplant. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2017;12(1):44–50. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- ICKSH-2023-04/grants from the Korean Society of Hematology Research Fund
- NRF-2021R1C1C1012397/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government
- 2024/research fund of Chungnam National University
- RS-2020-KH088690/Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI) funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

