Unmasking the uncommon: Merkel cell carcinoma mimicking benign upper lip swelling in an elderly patient
- PMID: 40814532
- PMCID: PMC12349789
- DOI: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1586_24
Unmasking the uncommon: Merkel cell carcinoma mimicking benign upper lip swelling in an elderly patient
Abstract
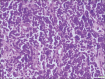
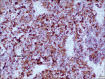
Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is a rare neuroendocrine carcinoma with aggressive behavior that predominantly affects the sun-damaged skin of the head and neck regions, extremities, and trunk of white older individuals. We present a unique case of MCC presenting as painless upper lip swelling, initially mistaken for a benign lesion. Histopathological examination revealed characteristic features of MCC. Early diagnosis and intervention led to improved outcomes. This case emphasizes the importance of considering MCC in the differential diagnosis of seemingly innocuous cutaneous lesions. To the best of our knowledge, 24 cases of MCC of the lips have been reported to date in the English language literature, and this case is probably the first to be reported from the Middle East region.
Keywords: Elderly; Merkel cell carcinoma; lip.
Copyright: © 2025 Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
An unusual case of Merkel cell carcinoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2008 Feb;134(2):119-23. doi: 10.1007/s00432-007-0257-2. Epub 2007 Jul 25. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2008. PMID: 17653576 Free PMC article.
-
Atypical presentation of Merkel cell carcinoma with pulmonary embolism.Oxf Med Case Reports. 2025 Aug 20;2025(8):omaf076. doi: 10.1093/omcr/omaf076. eCollection 2025 Aug. Oxf Med Case Reports. 2025. PMID: 40843046 Free PMC article.
-
Severe Relapsing Hailey-Hailey Disease Displaying a Durable Complete Response to Hydroxyurea.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2024 Nov;32(3):168-169. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2024. PMID: 40654217
-
Sun protection for preventing basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jul 25;7(7):CD011161. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011161.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27455163 Free PMC article.
-
Cabozantinib for different endocrine tumours: killing two birds with one stone. A systematic review of the literature.Endocrine. 2024 Jan;83(1):26-40. doi: 10.1007/s12020-023-03526-0. Epub 2023 Oct 18. Endocrine. 2024. PMID: 37851242 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Toker C. Trabecular carcinoma of the skin. Arch Dermatol. 1972;106:501–4. [doi: 10.1001/archderm.1972.01620160039008] - PubMed
-
- Chiarelli TG, Grant-Kels JM, Sporn JR, Rezuke WN, Whalen JD. Unusual presentation of a Merkel cell carcinoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;42:366–70. [doi: 10.1016/S0190-9622(00)90114-2] - PubMed
-
- Pulitzer MP, Amin BD, Busam KJ. Merkel Cell Carcinoma: Review. Adv Anat Pathol. 2009;16:135–44. [doi: 10.1097/PAP] - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
