Global insights on the diagnosis, management, and prevention of pediatric ingestions: A report from the FISPGHAN expert panel
- PMID: 40814587
- PMCID: PMC12350048
- DOI: 10.1002/jpr3.70025
Global insights on the diagnosis, management, and prevention of pediatric ingestions: A report from the FISPGHAN expert panel
Abstract
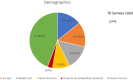
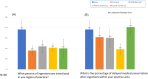
This is a comprehensive review of pediatric foreign body (FB) ingestions, emphasizing the global burden, epidemiology, and management strategies. Predominantly occurring in children under 6, with a peak between 6 months and 3 years, these incidents pose significant health risks with substantial regional variations in ingested objects-ranging from household items to caustic substances. The pathophysiological effects of ingestions are outlined, highlighting specific dangers associated with button batteries, sharp objects, and caustic agents, which can lead to severe tissue damage and long-term complications. A survey of (70) pediatric gastroenterologists from FISPGHAN societies revealed varied regional practices in the frequency of different FB ingestions with food impaction highest in North America and Ocenaia and caustic ingestion more common is Asia. Button batterers were serious concerns across all regions. Management approaches, specifically intubation practice varied across regions. A review of management protocols for different types of ingestions are provided, emphasizing the urgency of endoscopic removal and follow-up care. Prevention strategies are critical, with a focus on public health interventions, legislation, and education to mitigate the risks associated with FB and caustic ingestions. This report underscores the need for enhanced preventive measures and uniform management guidelines to reduce the incidence and improve outcomes of pediatric ingestions worldwide.
Keywords: button battery; caustic; foreign body removal; magnet ingestion; water beads.
© 2025 The Author(s). JPGN Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition and the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Orsagh‐Yentis D, McAdams RJ, Roberts KJ, McKenzie LB. Foreign‐body ingestions of young children treated in US Emergency Departments: 1995‐2015. Pediatrics. 2019;143(5):e20181988. - PubMed
-
- Jayachandra S, Eslick GD. A systematic review of paediatric foreign body ingestion: presentation, complications, and management. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2013;77(3):311‐317. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

