Economic Evaluation of System-Wide Implementation of Kidney Supportive Care
- PMID: 40814623
- PMCID: PMC12348168
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2025.05.022
Economic Evaluation of System-Wide Implementation of Kidney Supportive Care
Abstract
Introduction: This evaluation explored the economic value of kidney supportive care (KSC) in patients with end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) receiving dialysis or conservative management for ESKD in the public health system of New South Wales, Australia.
Methods: Deidentified patient-level data were extracted from a linked dataset of admitted and nonadmitted patient data, emergency department episodes, and death registrations. Data between 1 July 2015 and 30 June 2019 were compared with usual treatment prior to statewide KSC implementation in the 2015-2016 financial years. A cost-benefit analysis model estimated the current economic value of KSC (1 July 2015 to 30 June 2019) and projected value to 30 June 2030 under different scenarios.
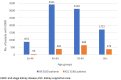
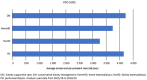
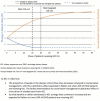
Results: The proportion of all patients with ESKD receiving KSC increased from 5% in 2015 to 2016 (n = 443) to 16% by 2018 to 2019. Over this period, KSC was estimated to increase survival by 3 to 21 weeks, depending on patient characteristics. Projections showed that continued delivery of KSC, with ESKD treatment modality patterns and costs remaining stable, would deliver a net economic benefit of A$ 109 million through avoided costs of care and return on investment (ROI) of 212%. When adjusted to include survival improvements attributable to KSC, the net economic benefit increased to A$ 275 million (ROI: 535%).
Conclusion: Economic evaluation of the statewide KSC service showed survival benefits and a net economic benefit 4 years after implementation. Net economic value over 10 years was estimated at A$ 275 million, which would increase with greater participation of patients with ESKD suitable for KSC.
Keywords: chronic kidney failure; cost-benefit analysis; kidney supportive care.
Crown Copyright © 2025 Published by Elsevier Inc. on behalf of the International Society of Nephrology.
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organization The top 10 causes of death. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death
-
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare Chronic kidney disease: Australian facts; 2023. How Many People Are Living With Chronic Kidney Disease in Australia? https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports/chronic-kidney-disease/chronic-kidney-di...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

