Japanese Patients' Perceptions of Shared Decision-Making in Renal Replacement Therapy
- PMID: 40814626
- PMCID: PMC12348115
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2025.05.011
Japanese Patients' Perceptions of Shared Decision-Making in Renal Replacement Therapy
Abstract
Introduction: Shared decision-making (SDM) is a key process in selecting renal replacement therapy (RRT). This study analyzed SDM perceptions, preferences, as well as patient- and facility-level factors influencing SDM perception among Japanese patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) who selected RRT.
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional survey of 475 adult patients with CKD from 49 medical facilities. SDM awareness and recognition, preferences for SDM timing and frequency, discussion content, and desired professional involvement were assessed. Patient- and facility-level factors associated with SDM perceptions were evaluated using multivariable analysis.
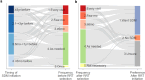
Results: The mean participant age was 67.4 years. Hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, and kidney transplantation were chosen by 71%, 24.4%, and 4.4% of patients, respectively. Although 81.2% recalled SDM occurring during RRT selection, only 4.7% were well aware of SDM before the survey. Patients prioritized discussions about daily life impact, financial burden, and family-related concerns. Most patients preferred SDM initiation when RRT was imminent, and to be conducted over multiple sessions. Many patients valued the involvement of medical social workers and their usual nonnephrologist physicians in addition to nephrologists. Multiple outpatient visits for RRT selection, involving nurse participation and extended consultation times, were significantly associated with SDM perceptions (prevalence ratio [PR]: 1.59, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.05-2.42).
Conclusion: Many Japanese patients with CKD retrospectively evaluated RRT selection as involving SDM; however, a few were familiar with the concept beforehand. This underscores the importance of establishing systems that facilitate repeated SDM discussions at critical moments for patients. These discussions should emphasize the impact of RRT on patients' lives and involve a multidisciplinary team.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; health care professionals; patient preferences; renal replacement therapy; shared decision-making.
© 2025 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Sakurada T., Koitabashi K., Murasawa M., Kohatsu K., Kojima S., Shibagaki Y. Effects of one-hour discussion on the choice of dialysis modality at the outpatient clinic: a retrospective cohort study using propensity score matching. Ther Apher Dial. 2023;27:442–451. doi: 10.1111/1744-9987.13941. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

