Validating 8 Area-Based Measures of Social Risk for Predicting Health and Mortality
- PMID: 40815521
- PMCID: PMC12357199
- DOI: 10.1001/jamahealthforum.2025.2669
Validating 8 Area-Based Measures of Social Risk for Predicting Health and Mortality
Abstract
Importance: Area-based measures of social risk are increasingly being used in policy applications in the US. While several have been demonstrated to be predictive of health and mortality in the general population, there is a need to identify area-based measures that are most reliable for policy applications, including measures that are associated with health and mortality consistently across subpopulations.
Objective: To compare the relative strength with which area and individual social risk measures are correlated with health outcomes and mortality, and the extent to which these associations are consistent across race, ethnicity, rurality, age, and gender.
Design, setting, and participants: This cross-sectional study included a sample of patients from primary care clinics across all 50 states that are part of the PRIME registry using electronic health records (2019-2021) linked to US Census Bureau restricted-use data at the individual level from 947 US primary care practices.
Exposures: Eight commonly used area based measures of social risk were examined: (1) Social Deprivation Index, (2) Social Vulnerability Index, (3) Area Deprivation Index (from University of Wisconsin), (4) Area Deprivation Index (constructed using Gophal Singh's original design), (5) Neighborhood Stress Score, (6) Index of Concentration at the Extremes for race and income, (7) French Index of Social Deprivation, and (8) the Community Resilience Estimates. Individual socioeconomic measures of education, poverty, and occupation were also examined.
Main outcomes and measures: Hypertension, diabetes, and chronic kidney disease derived from electronic health records, and mortality from the Census Numident.
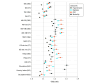
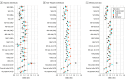
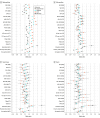
Results: Data from 2 801 000 patients were analyzed. Among these, 44% were male individuals and 56% were female individuals; 20% were younger than 25 years, 23% were aged 25 to 44 years, 30% were aged 45 to 64 years, and 27% were aged 65 years and older; 0.5% were American Indian or Alaskan Native, 2.1% Asian, 7.6% Black, 0.2% Native Hawaiian and Pacific Islander, 0.03% were 2 or more races, and 70% were White. Area-based measures of social risk were generally better predictors of hypertension, diabetes, and chronic kidney disease, whereas individual socioeconomic measures were generally better predictors of mortality. The strongest predictor across health outcomes was the Area Deprivation Index, and that Gopal Singh's version was the most equitably predictive across rural areas and across all racial and ethnic subgroups.
Conclusions and relevance: In this cross-sectional study, area-based measures predicted health outcomes better than individual socioeconomic measures, and generally predicted health equitably across subpopulations; thus, their use should be considered in conjunction or instead of using individual-level measures for selected health policy applications.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
A New Measure of Quantified Social Health Is Associated With Levels of Discomfort, Capability, and Mental and General Health Among Patients Seeking Musculoskeletal Specialty Care.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 Apr 1;483(4):647-663. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003394. Epub 2025 Feb 5. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 39915110
-
Area Vulnerability and Disparities in Therapy for Patients With Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma.JAMA Netw Open. 2024 Apr 1;7(4):e248747. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.8747. JAMA Netw Open. 2024. PMID: 38687479 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral interventions to reduce risk for sexual transmission of HIV among men who have sex with men.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Jul 16;(3):CD001230. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001230.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008. PMID: 18646068
-
Racial and Ethnic Minorities Underrepresented in Pain Management Guidelines for Total Joint Arthroplasty: A Meta-analysis.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Sep 1;482(9):1698-1706. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003026. Epub 2024 Mar 18. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 38497759 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Phillips JRL, Ostrovsky A, Bazemore AW. Adjusting Medicare payments for social risk to better support social needs. Health Aff Forefr. Published online June 1, 2021. doi: 10.1377/forefront.20210526.933567 - DOI
-
- Breslau J, Martin L, Timbie J, Qureshi N, Zajdman D. Landscape of Area-Level Deprivation Measures and Other Approaches to Account for Social Risk and Social Determinants of Health in Health Care Payments. RAND Health Care; 2022.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

