Protocol for vibratome sectioning, immunofluorescence, and S-phase labeling of inner ear organoids
- PMID: 40815565
- PMCID: PMC12392772
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xpro.2025.104032
Protocol for vibratome sectioning, immunofluorescence, and S-phase labeling of inner ear organoids
Abstract
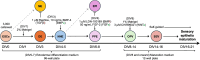
Inner ear organoids represent a potentially inexhaustible source of otic tissues, including sensory hair cells and supporting cells, for in vitro manipulation. Here, we present a protocol for labeling S-phase entry of cells in inner ear organoids using 5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine (EdU), followed by fixation and vibratome sectioning. Nuclear EdU is then detected alongside protein markers of interest via immunofluorescence. This workflow enables the visualization of cell and tissue morphologies within developing organoids and assessment of how different manipulations affect cell proliferation. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Matern et al.1.
Keywords: Cell Differentiation; Cell culture; Developmental biology; Model Organisms; Molecular/Chemical Probes; Organoids; Stem Cells; Tissue Engineering.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
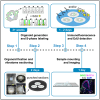
 ’ indicates pathway activation and ‘
’ indicates pathway activation and ‘ ’ indicates pathway inhibition.
’ indicates pathway inhibition.



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

