Alpha-synuclein abundance and localization are regulated by the RNA-binding protein PUMILIO1
- PMID: 40815569
- PMCID: PMC12422362
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.116145
Alpha-synuclein abundance and localization are regulated by the RNA-binding protein PUMILIO1
Abstract
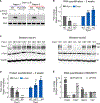
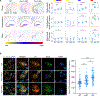
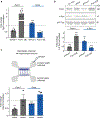
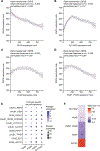
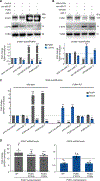
The protein α-synuclein, encoded by SNCA, accumulates in Parkinson's disease (PD) and other synucleinopathies for reasons that remain unclear. Here, we investigated whether SNCA is regulated in vivo by the RNA-binding protein PUM1. We establish that PUM1 binds to SNCA's 3' UTR in mouse and human cells. In induced neurons from patients with SNCA locus triplication, PUM1 mRNA levels are lower than in healthy controls, but increasing PUM1 normalizes both SNCA mRNA and α-synuclein protein levels, largely by suppressing the long 3' UTR SNCA isoform. In microfluidic chamber experiments, silencing PUM1 causes a redistribution of SNCA between the soma and axons. We also show that the previously described miR-7 regulation of SNCA mRNA requires PUM1. Lastly, we report finding several individuals with PD in clinical databases bearing variants in PUM1 that affect its RNA-binding ability. Understanding how RNA-binding proteins regulate α-synuclein could lead to viable new therapies for synucleinopathies.
Keywords: AGO2; CP: Molecular biology; CP: Neuroscience; PUM1; Parkinson’s disease; RNA-binding protein; SNCA; alpha-synuclein; miR-7.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests V.K. is a co-founder of DaCapo Brainscience, a company involved in neurodegenerative disease research.
Figures


References
-
- Hickman RA, Faust PL, Marder K, Yamamoto A, and Vonsattel JP (2022). The distribution and density of Huntingtin inclusions across the Huntington disease neocortex: regional correlations with Huntingtin repeat expansion independent of pathologic grade. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 10, 55. 10.1186/s40478-022-01364-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ibanez P, Lesage S, Janin S, Lohmann E, Durif F, Destee A, Bonnet AM, Brefel-Courbon C, Heath S, Zelenika D, et al. (2009). Alpha-synuclein gene rearrangements in dominantly inherited parkinsonism: frequency, phenotype, and mechanisms. Arch. Neurol. 66, 102–108. 10.1001/archneurol.2008.555. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F31 NS113574/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AG000222/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007088/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS119690/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS128142/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS125018/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- TL1 TR001875/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS109858/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 NS036630/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD016167/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA251753/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 NS064928/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS036630/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM145279/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

