Comparative real-world outcomes of CD19-directed CAR T-cell therapies in large B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 40815804
- PMCID: PMC12615284
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2025016778
Comparative real-world outcomes of CD19-directed CAR T-cell therapies in large B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
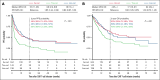
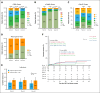
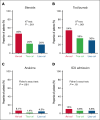
Although 3 commercial CD19-targeted chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies are available for large B-cell lymphomas (LBCLs), no randomized clinical trials have compared their efficacy and safety. In this retrospective multicenter cohort study, we evaluated real-world clinical outcomes of patients with relapsed/refractory LBCL treated with axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel), tisagenlecleucel (tisa-cel), or lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel). Between April 2016 and July 2024, 624 patients received CD19-targeted CAR T-cell therapies (344 axi-cel, 142 tisa-cel, and 138 liso-cel). At a median follow-up of 20.9 months, the respective estimated 2-year progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) rates were 46% and 63% for axi-cel, 30% and 45% for tisa-cel, and 45% and 58% for liso-cel. After adjusting for potential confounders in multivariate analyses, tisa-cel was associated with inferior PFS and OS compared to axi-cel. No significant survival differences were found between liso-cel and axi-cel. Propensity score and subanalyses of patients treated in the second-line vs third-line or later settings yielded similar outcomes. Compared to axi-cel, the objective response rate at 100 days was higher for liso-cel and lower for tisa-cel. Rates of cytokine release syndrome, immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome, and immune effector cell-associated hematotoxicity, and febrile neutropenia were significantly higher with axi-cel. However, no significant differences in the cumulative incidence of infections or nonrelapse mortality were found. Axi-cel was associated with faster vein-to-vein time (axi-cel, 35 days; tisa-cel, 43 days; liso-cel, 41 days) and fewer out-of-specification products (axi-cel, 2%; tisa-cel, 4%; liso-cel, 11%). These results provide insights into potential differential outcomes depending on product selection.
© 2025 American Society of Hematology. Published by Elsevier Inc. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: X.D.-S. has served on advisory boards for Kite/Gilead; and has received speaker honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb and Hoffmann-La Roche. M.S. served as a paid consultant for McKinsey & Company, Angiocrine Bioscience Inc, and Omeros Corporation; reports research funding from Angiocrine Bioscience Inc, Omeros Corporation, Amgen Inc, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Sanofi; served on ad hoc advisory boards for Kite (a Gilead company) and Miltenyi Biotec; and reports honoraria from i3 Health, Medscape, CancerNetwork, Intellisphere LLC, Curio Science LLC, and IDEOlogy. M.-A.P. reports honoraria from Adicet, Allogene, Allovir, Caribou Biosciences, Celgene, Bristol Myers Squibb, Equilium, ExeVir, ImmPACT Bio, Incyte, Karyopharm, Kite/Gilead, Merck, Miltenyi Biotec, MorphoSys, Nektar Therapeutics, Novartis, Omeros, Orca Bio, Sanofi, Syncopation, VectivBio AG, and Vor Biopharma; serves on data and safety monitoring boards for Cidara Therapeutics and Sellas Life Sciences; participates on the scientific advisory board of NexImmune; reports ownership interests in NexImmune, Omeros, and Orca Bio; and institutional research support for clinical trials from Allogene, Incyte, Kite/Gilead, Miltenyi Biotec, Nektar Therapeutics, and Novartis. A.P.B. reports consultancy for Bristol Myers Squibb. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




References
-
- Schuster SJ, Bishop MR, Tam CS, et al. Tisagenlecleucel in adult relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(1):45–56. - PubMed
-
- Abramson JS, Palomba ML, Gordon LI, et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel for patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphomas (TRANSCEND NHL 001): a multicentre seamless design study. Lancet. 2020;396(10254):839–852. - PubMed
-
- Locke FL, Miklos DB, Jacobson CA, et al. Axicabtagene ciloleucel as second-line therapy for large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(7):640–654. - PubMed
-
- Kamdar M, Solomon SR, Arnason J, et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel versus standard of care with salvage chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplantation as second-line treatment in patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma (TRANSFORM): results from an interim analysis of an open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2022;399(10343):2294–2308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

